Setup and installation of 'Milvus DB: AI-Ready Vector Database Environment' on Azure
This section describes how to launch and connect to ‘Milvus DB: AI-Ready Vector Database Environment’ VM solution on Azure Platform.
- Open Milvus DB: AI-Ready Vector Database Environment VM listing on Azure Marketplace.
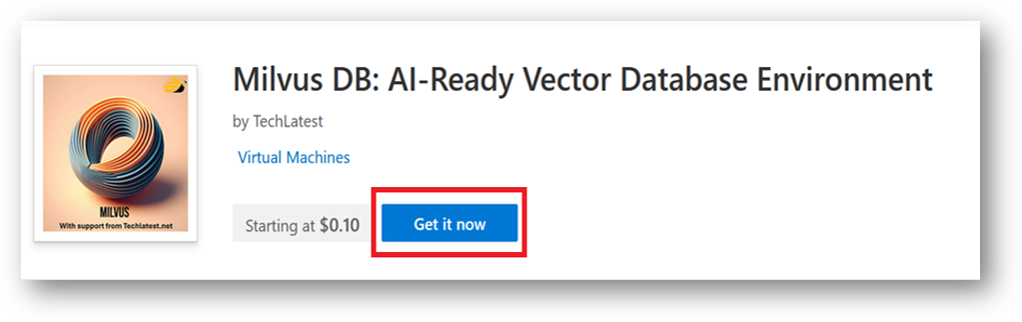
- Click on Get It Now
-
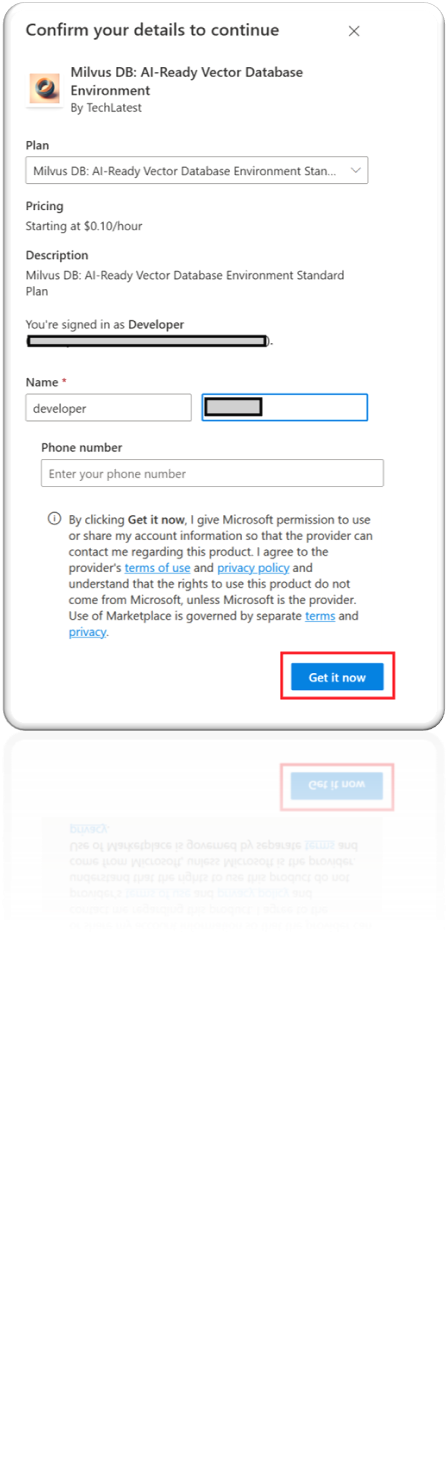
Login with your credentials, provide the details here. Once done click on Continue.
-
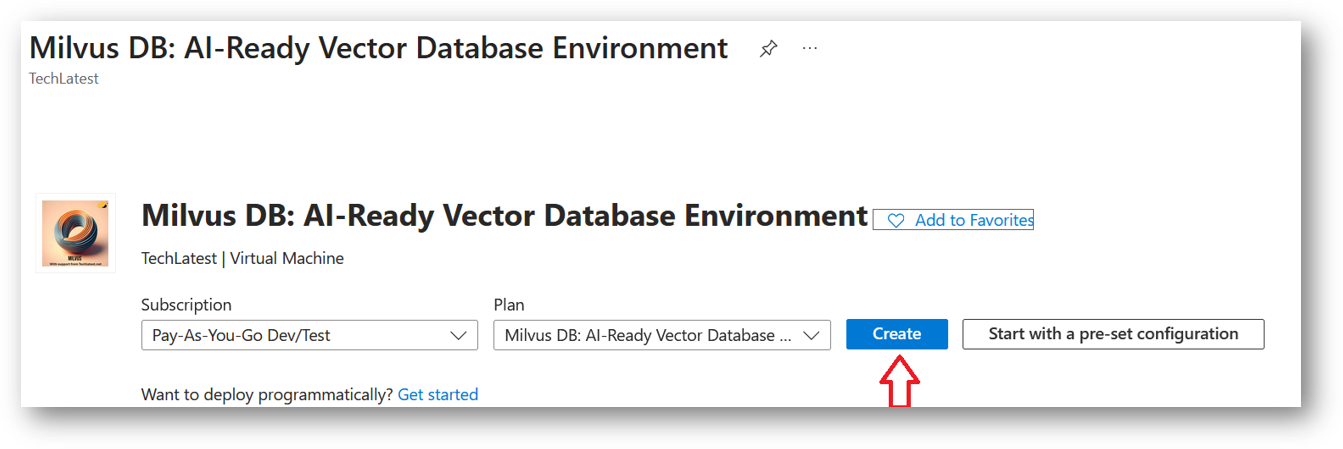
It will take you to the Product details page. Click on Create.
-
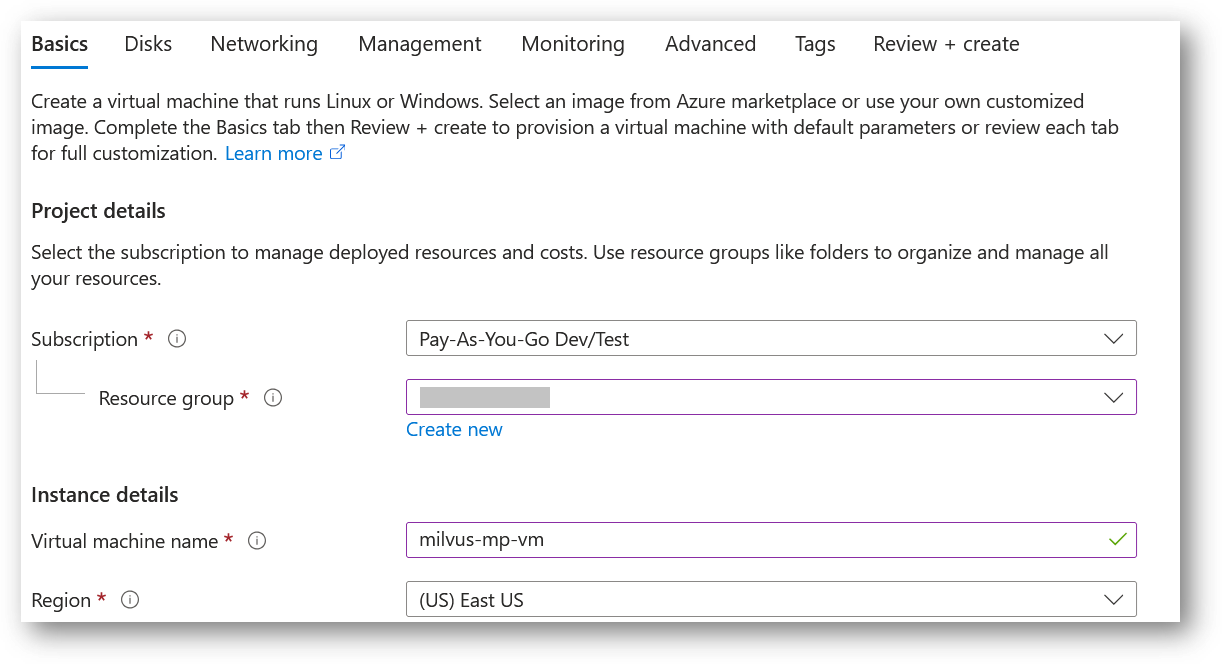
Select a Resource group for your virtual machine
-
Select a Region where you want to launch the VM(such as East US)
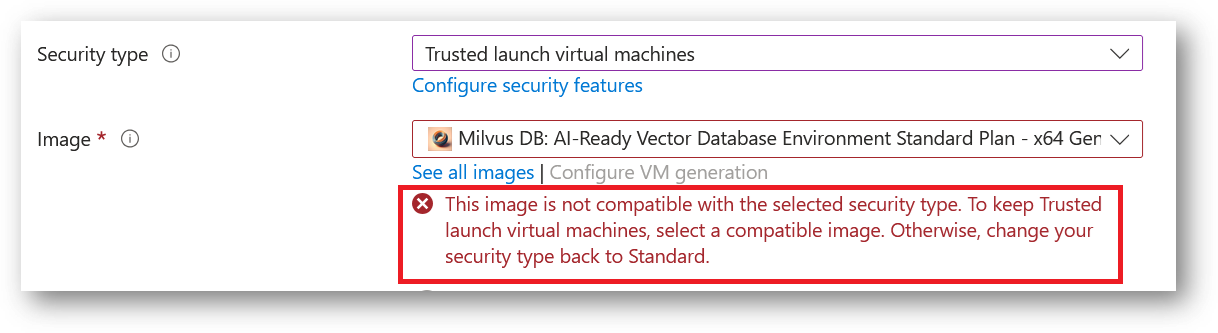
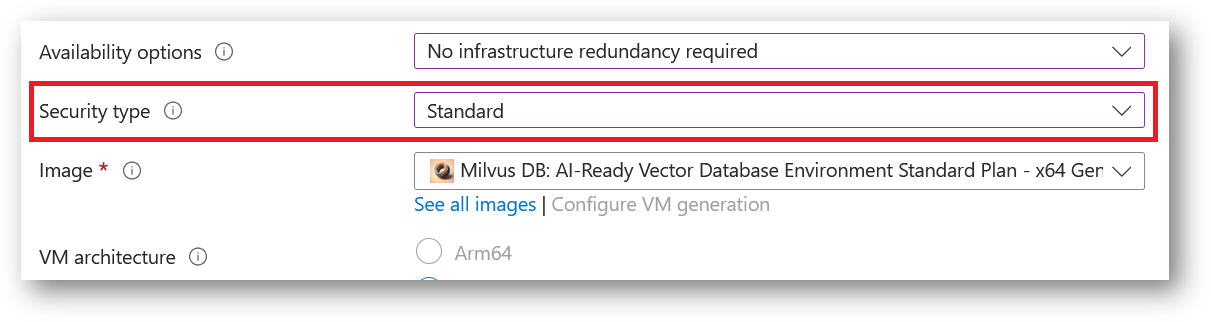
- Note: If you see “This image is not compatible with selected security type. To keep trusted launch virtual machines, select a compatible image. Otherwise change your security type back to Standard” error message below the Image name as shown in the screenshot below then please change the Security type to Standard.
- Optionally change the number of cores and amount of memory.
Minimum VM Specs : 8GB vRAM / 2vCPU, but for swift performace please choose 16GB vRAM/4vCPU configuration.
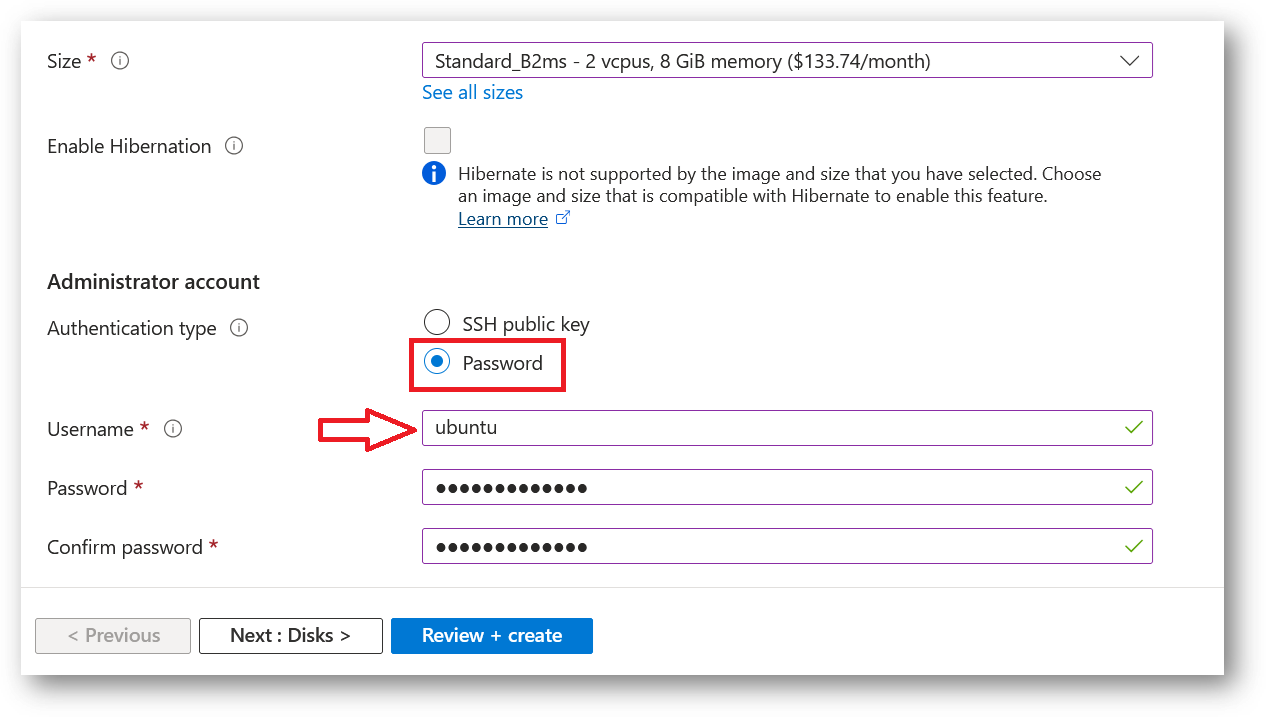
Select the Authentication type as Password and enter Username as ubuntu and Password of your choice.
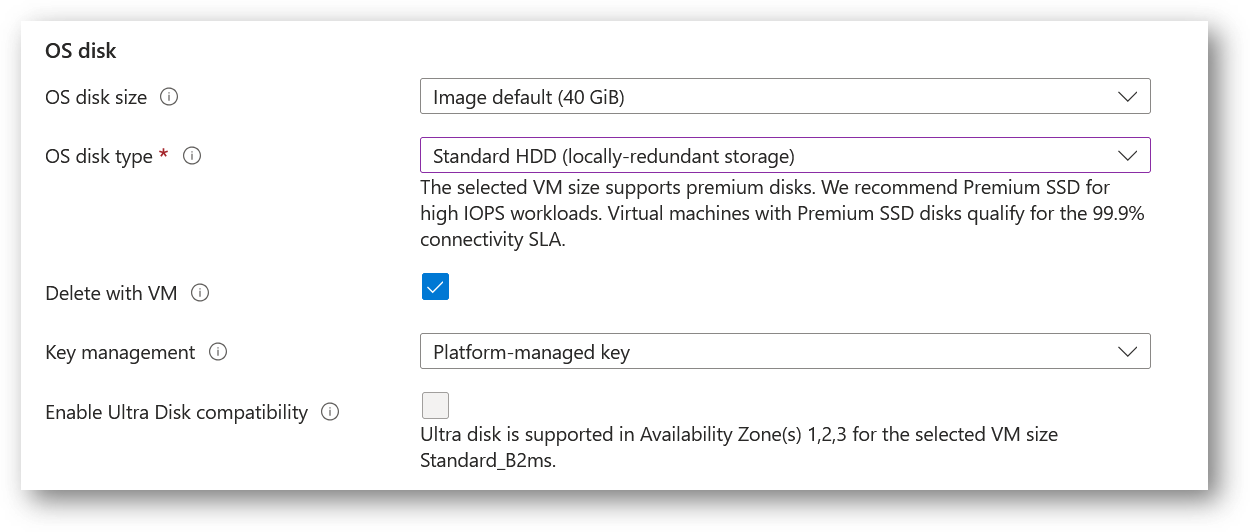
- Optionally change the OS disk size and its type. By default the VM comes with 40GB of disk.
- Optionally change the network and subnetwork names. Be sure that whichever network you specify has ports 22 (for ssh), 3389 (for RDP), port 80 (for HTTP) and 443 (for HTTPS) exposed.
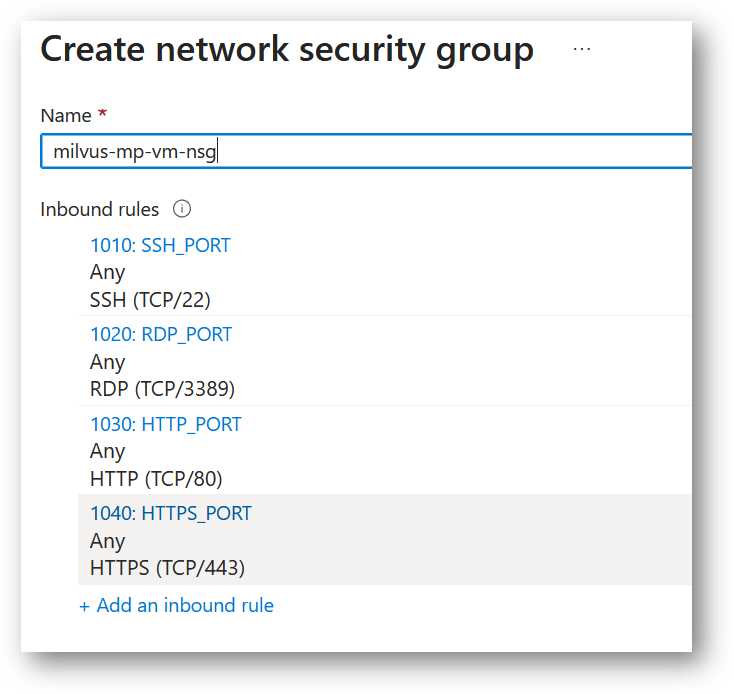
The VM comes with the preconfigured NSG rules. You can check them by clicking on Create New option available under the security group option.
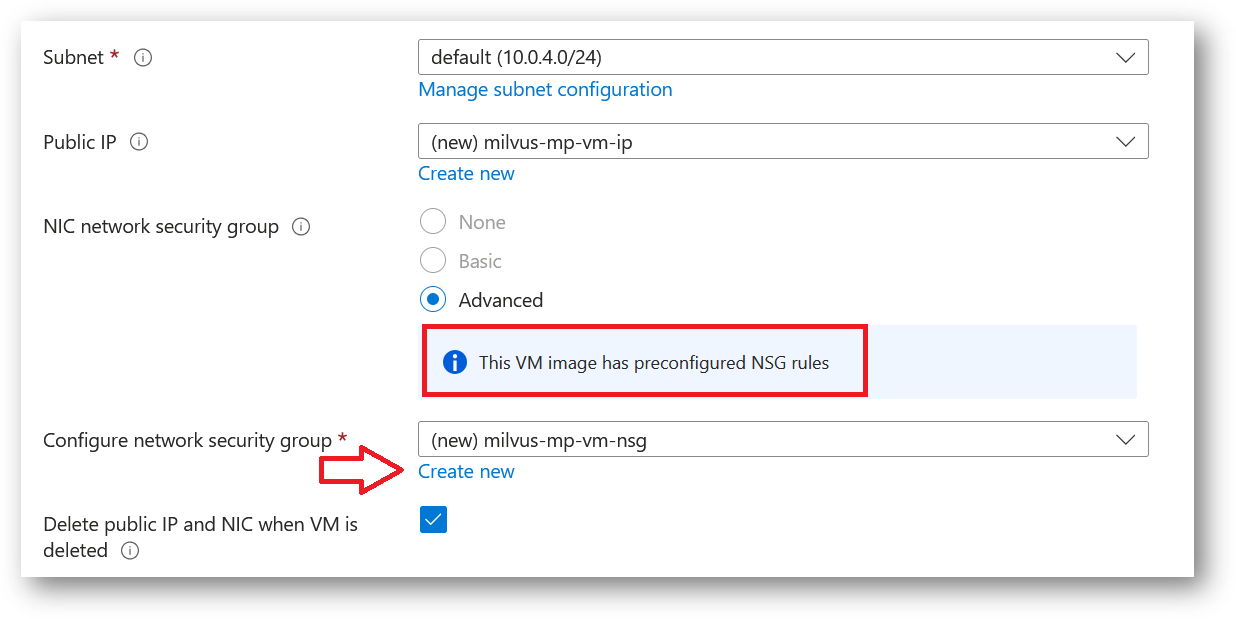
- Optionally go to the Management, Advanced and Tags tabs for any advance settings you want for the VM.
- Click on Review + create and then click on Create when you are done.
Virtual Machine will begin deploying.
- A summary page displays when the virtual machine is successfully created. Click on Go to resource link to go to the resource page. It will open an overview page of virtual machine.
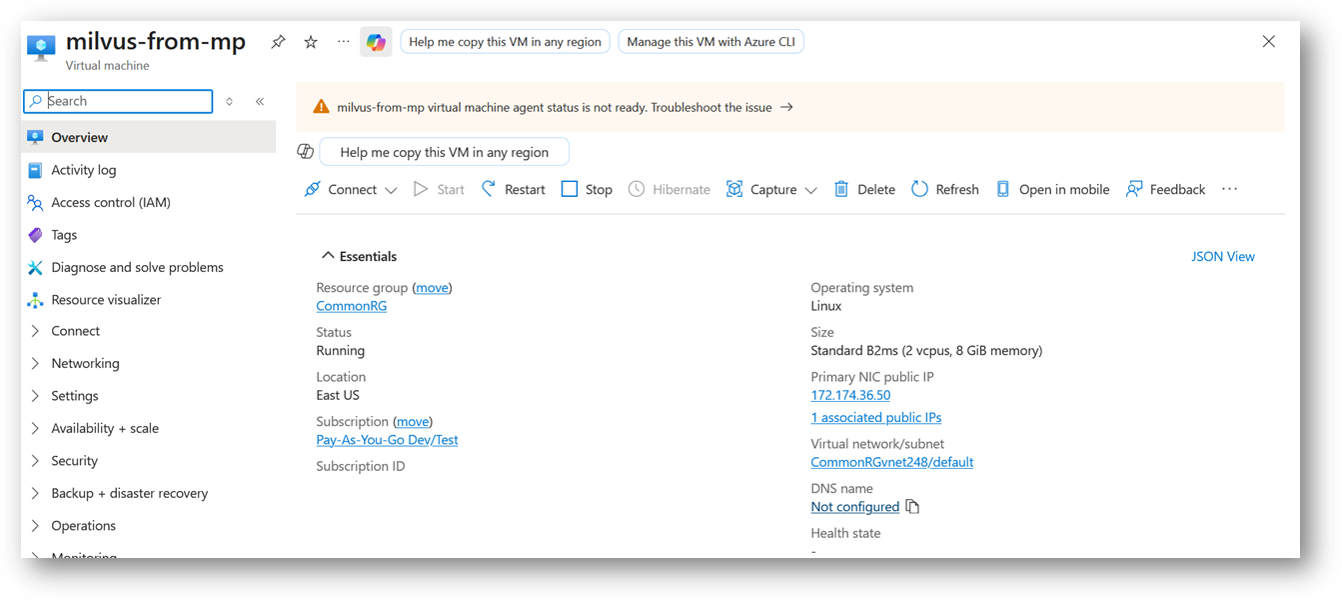
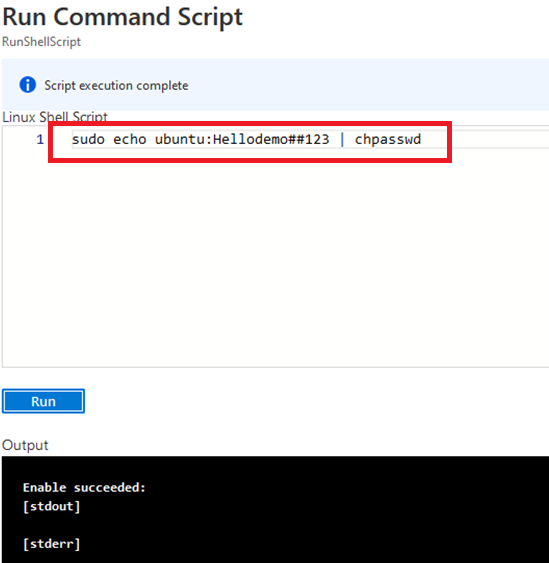
- If you want to update your password then open up the left navigation pane, select Run command, select RunShellScript and enter following command to change the password of the vm .
sudo echo ubuntu:yourpassword | chpasswd
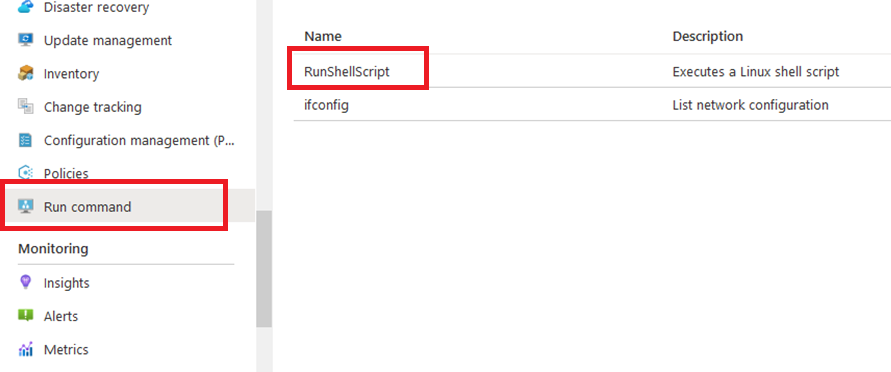
Now the password for ubuntu user is set, you can SSH to the VM. To do so, first note the public IP address of the VM from VM details page as highlighted below

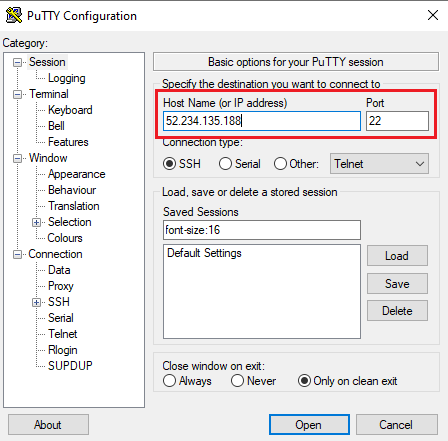
Open putty, paste the IP address and click on Open.
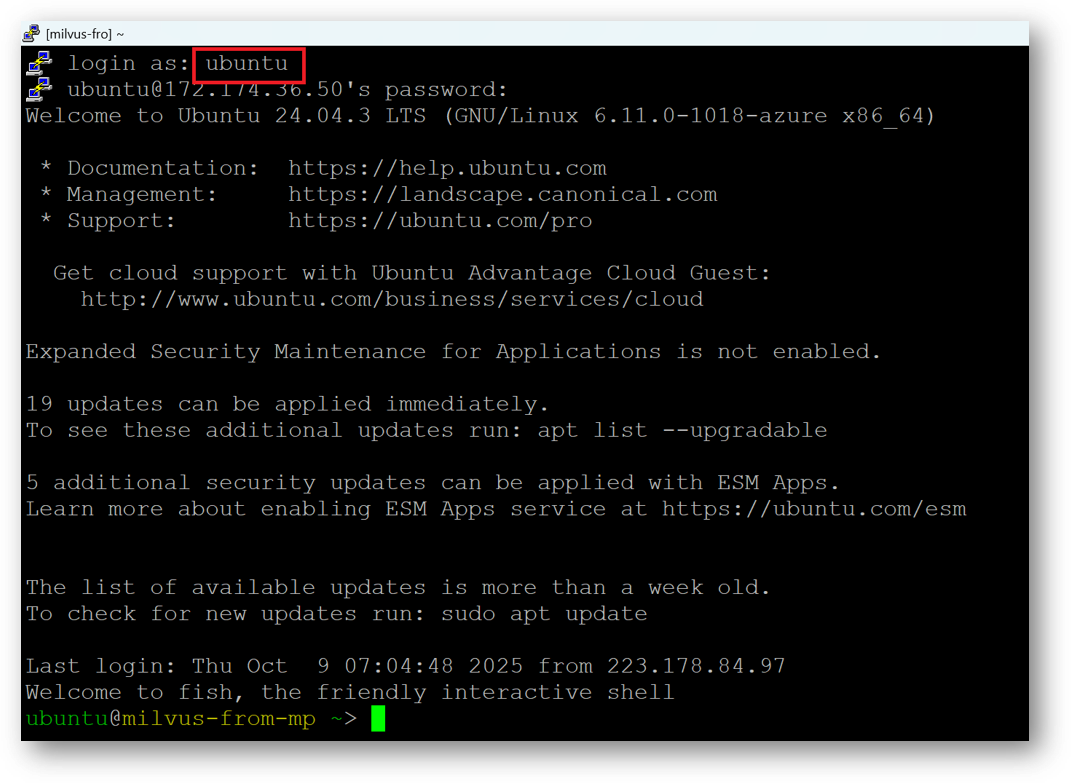
login as ubuntu and provide the password for ‘ubuntu’ user.
-
You can also connect to the VM’s desktop environment from any local windows machine using RDP protocol or local linux machine using Remmina.
-
To connect using RDP via Windows Machine, first note the public IP address of the VM from VM details page as highlighted below

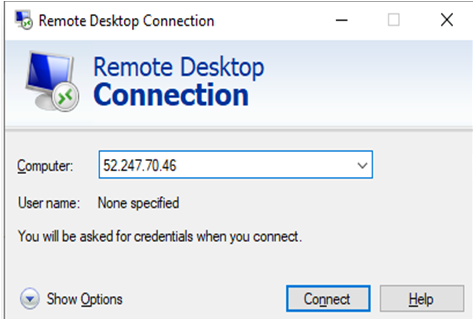
- Then From your local windows machine, goto “start” menu, in the search box type and select “Remote desktop connection”.
In the “Remote Desktop connection” wizard, copy the public IP address and click connect
- This will connect you to the VM’s desktop environment. Provide the username (e.g “ubuntu”) and the password set in the step4 to authenticate. Click OK
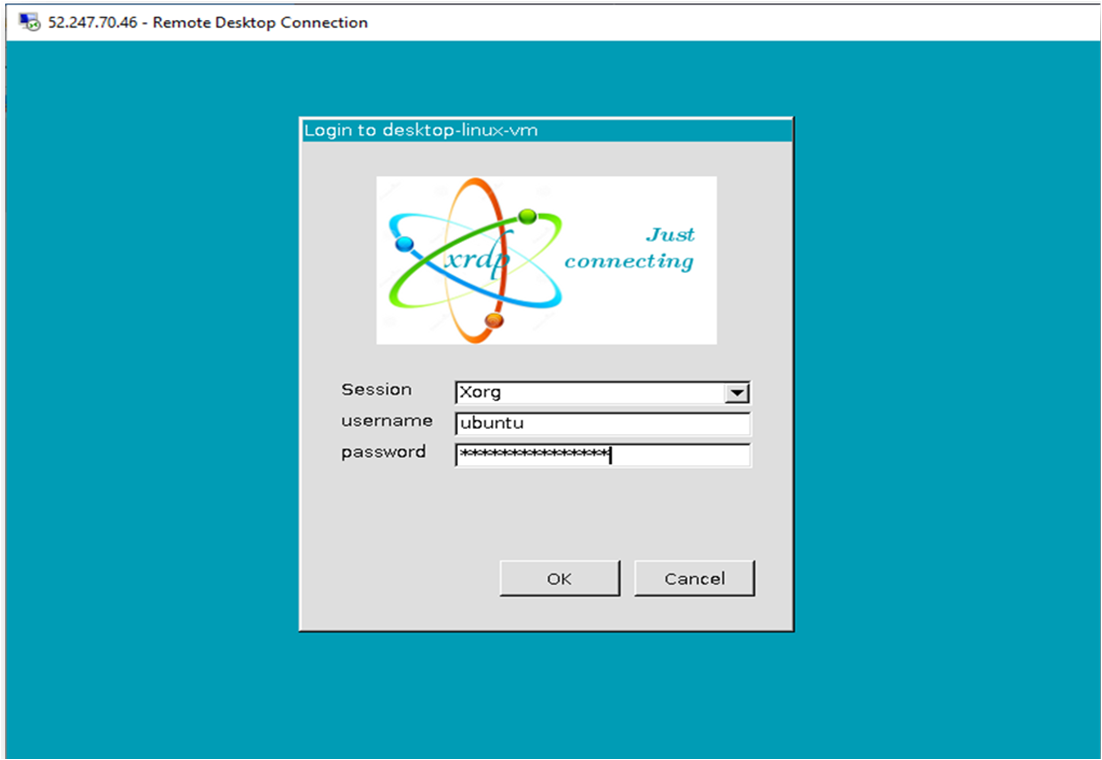
- Now you are connected to the out of box “Milvus DB: AI-Ready Vector Database Environment” VM’s desktop environment via Windows Machine.

- To connect using RDP via Linux machine, first note the external IP of the VM from VM details page, then from your local Linux machine, goto menu, in the search box type and select “Remmina”.
Note: If you don’t have Remmina installed on your Linux machine, first Install Remmina as per your linux distribution.
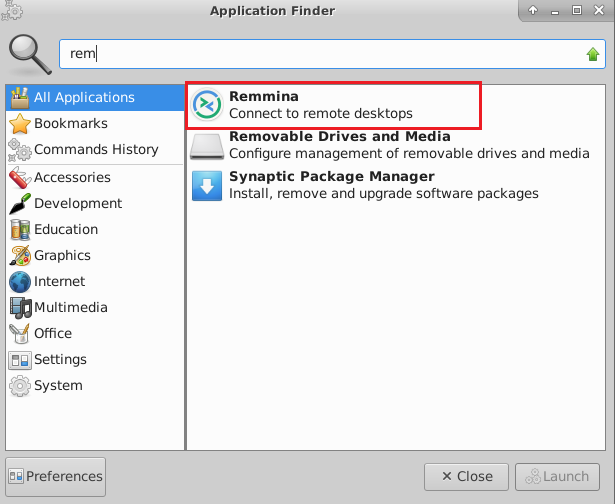
- In the “Remmina Remote Desktop Client” wizard, select the RDP option from dropdown and paste the external ip and click enter.
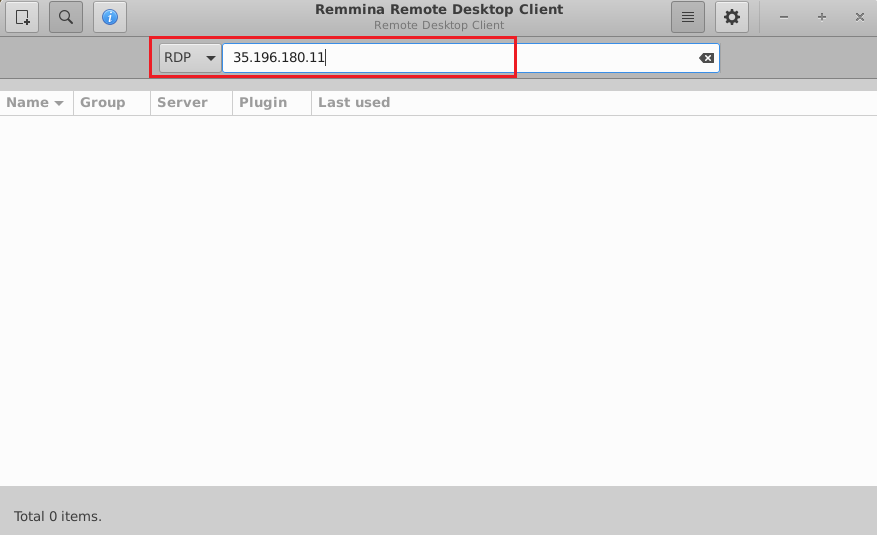
- This will connect you to the VM’s desktop environment. Provide “ubuntu” as the userid and the password set in above reset password step to authenticate. Click OK
- Now you are connected to out of box “Milvus DB: AI-Ready Vector Database Environment” VM’s desktop environment via Linux machine.

- Once you are in RDP session, Open the FireFox from RDP desktop and enter below url to access the Milvus Web UI.
http://localhost:9091/webui/
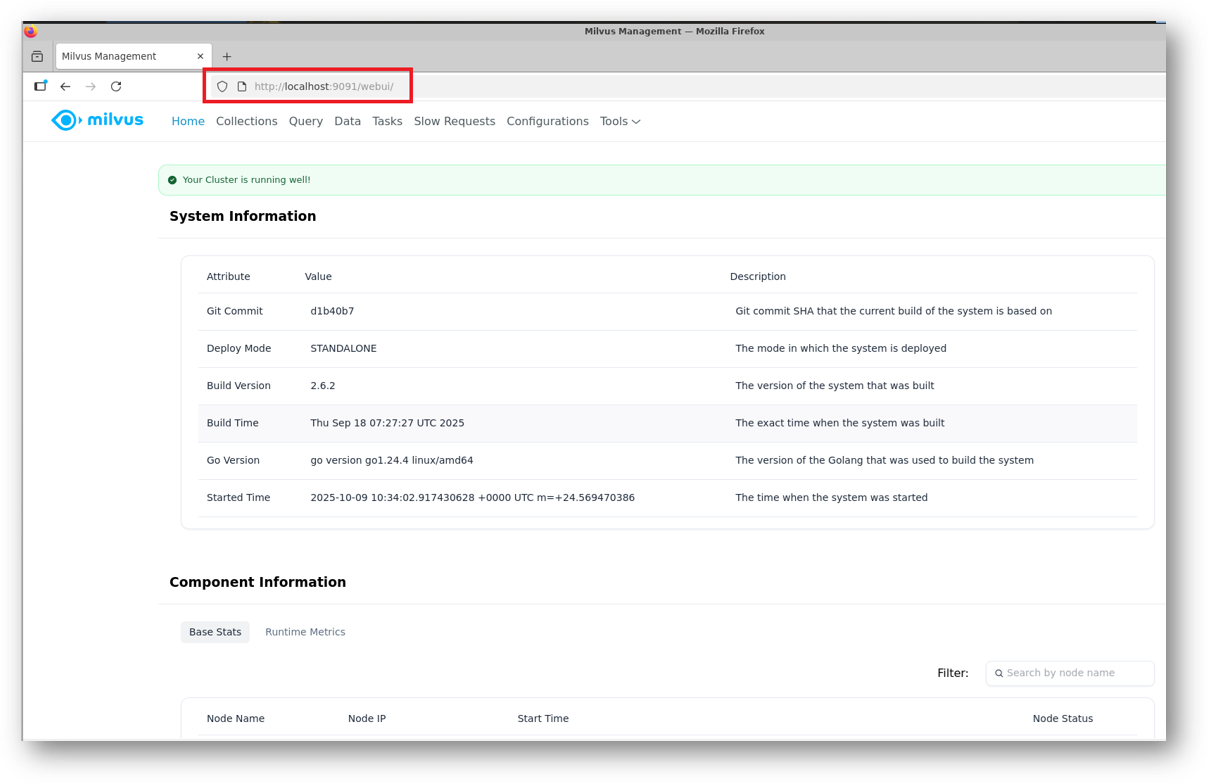
Note: Milvius UI is available only via RDP for security reasons. However if you want to access it publicly using Public IP of the VM in your local browser then please follow the steps given in Milvus WebUI Proxy Setup .
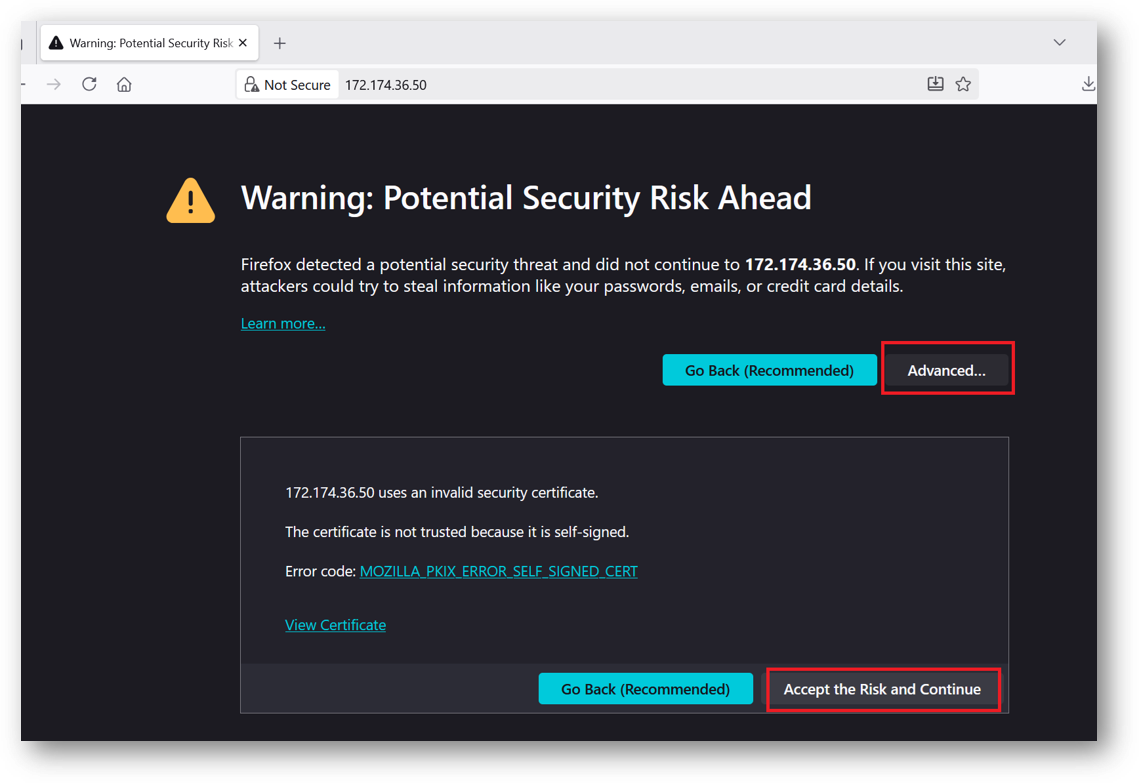
- To access the JupyterHub Web Interface, copy the public IP address of the VM and paste it in the browser as https://public_ip_of_vm.
Browser will display a SSL certificate warning message. Accept the certificate warning and Continue.
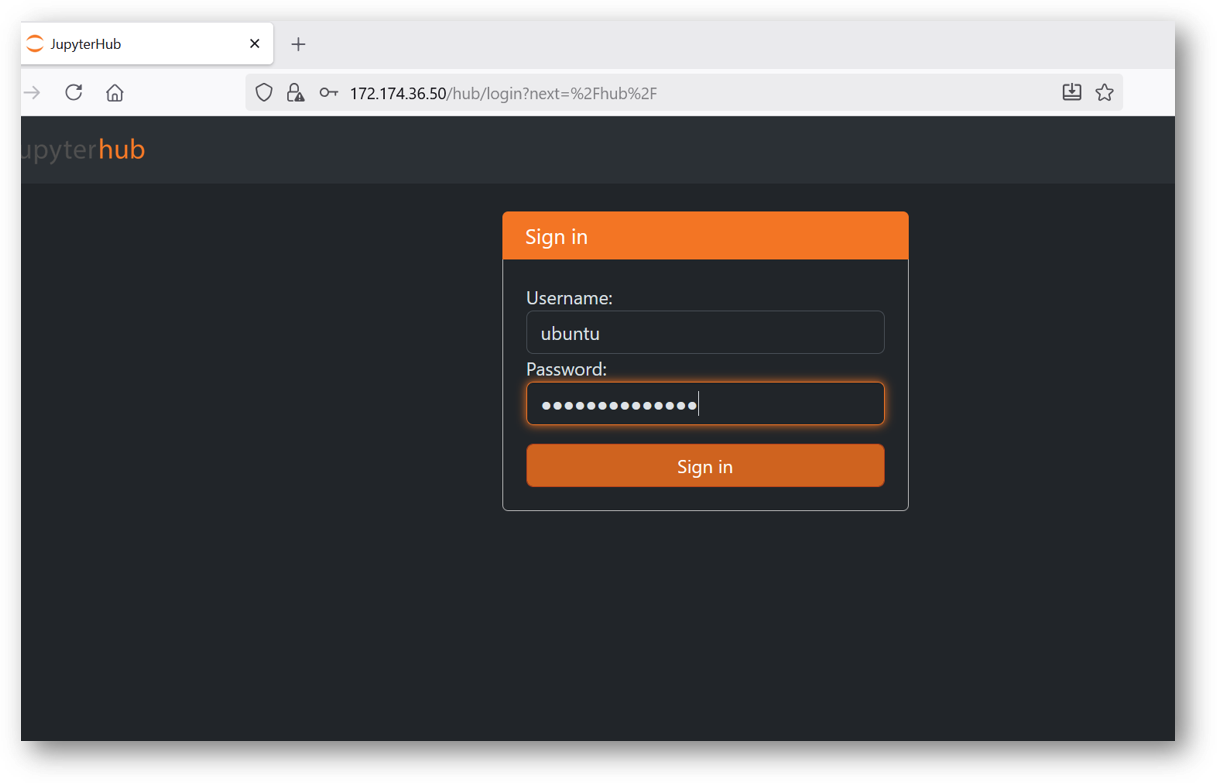
- Provide the ‘ubuntu’ user and its password set during VM creation. ubuntu is configured as an admin user here.
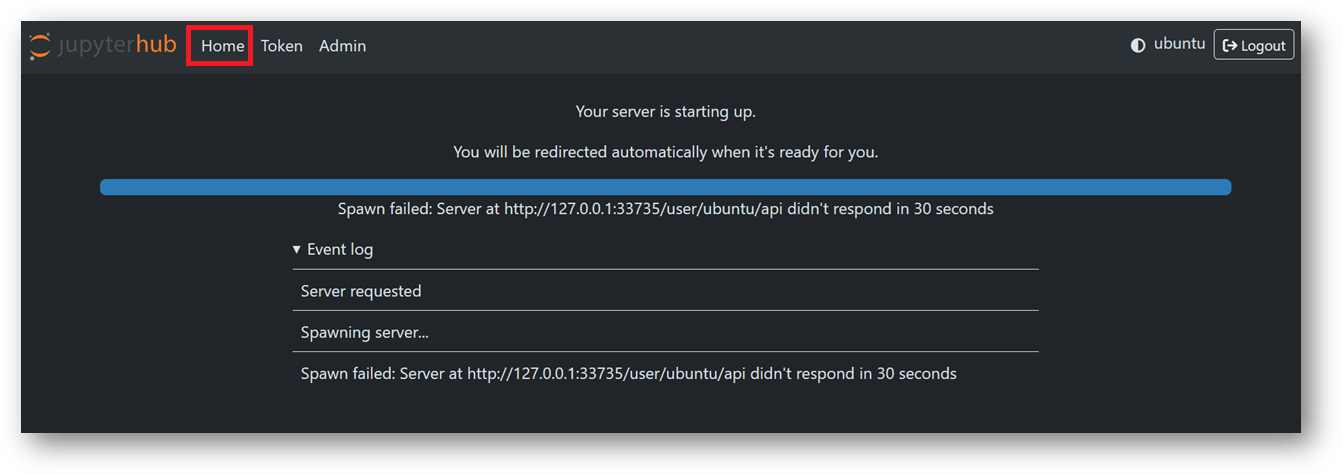
- If your jupyter server did not spawn in 30 sec you will see error message as shown in below screenshot. In this case simply click on Home tab and click Start My Server button. It will spawn the server again.
- Now you are logged in to jupyterhub. Here you can see we have setup folder configured with jupyter-venv, jupyterhub_config.py files along with other jupyterhub configuration files. You can use jupyter notebook to run and test your AI projects.
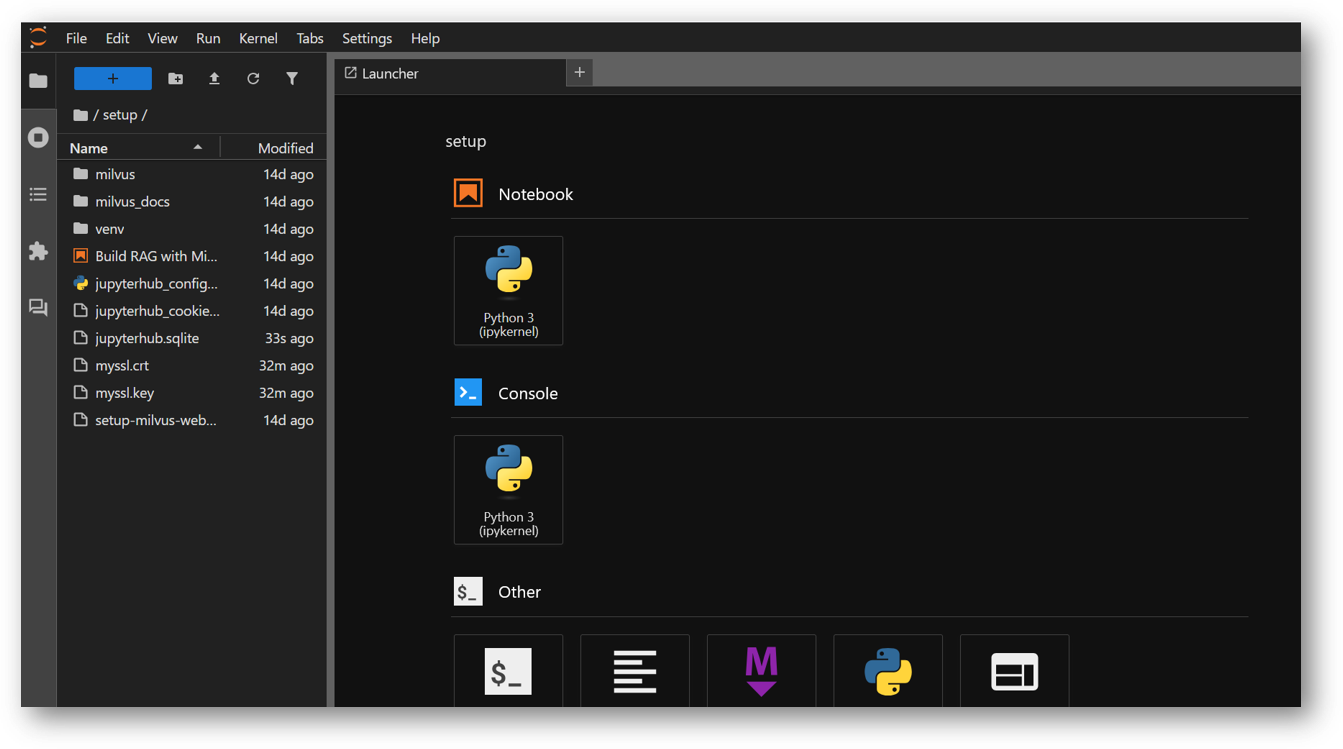
- The VM comes preloaded with “Build RAG with Milvus” example. The example file “Build RAG with Milvus and Ollama.ipynb” is available in /home/ubuntu/setup/ directory. Once you logged in the jupyterhub, navigate to setup directory and click on “Build RAG with Milvus and Ollama.ipynb” file.
In this example, we will show you how to build a RAG(Retrieval-Augmented Generation) pipeline with Milvus and Ollama.
The RAG system combines a retrieval system with a generative model to generate new text based on a given prompt. This example uses the FAQ pages from the Milvus Documentation 2.4.x as the private knowledge in our RAG for a simple RAG pipeline.
The documents are already Downloaded as a zip and extracted to the folder milvus_docs in the same setup directory. The example is using ollama local model to execute , so you don’t need to provide any API keys here.
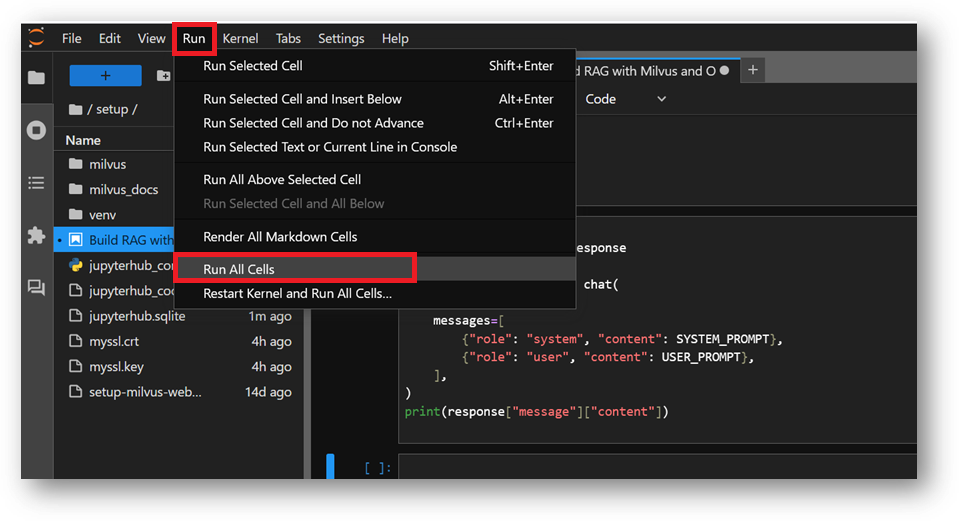
- You can simply run each cell one by one in same sequence or you can select the Run All Cells option from Run Menu at the top.
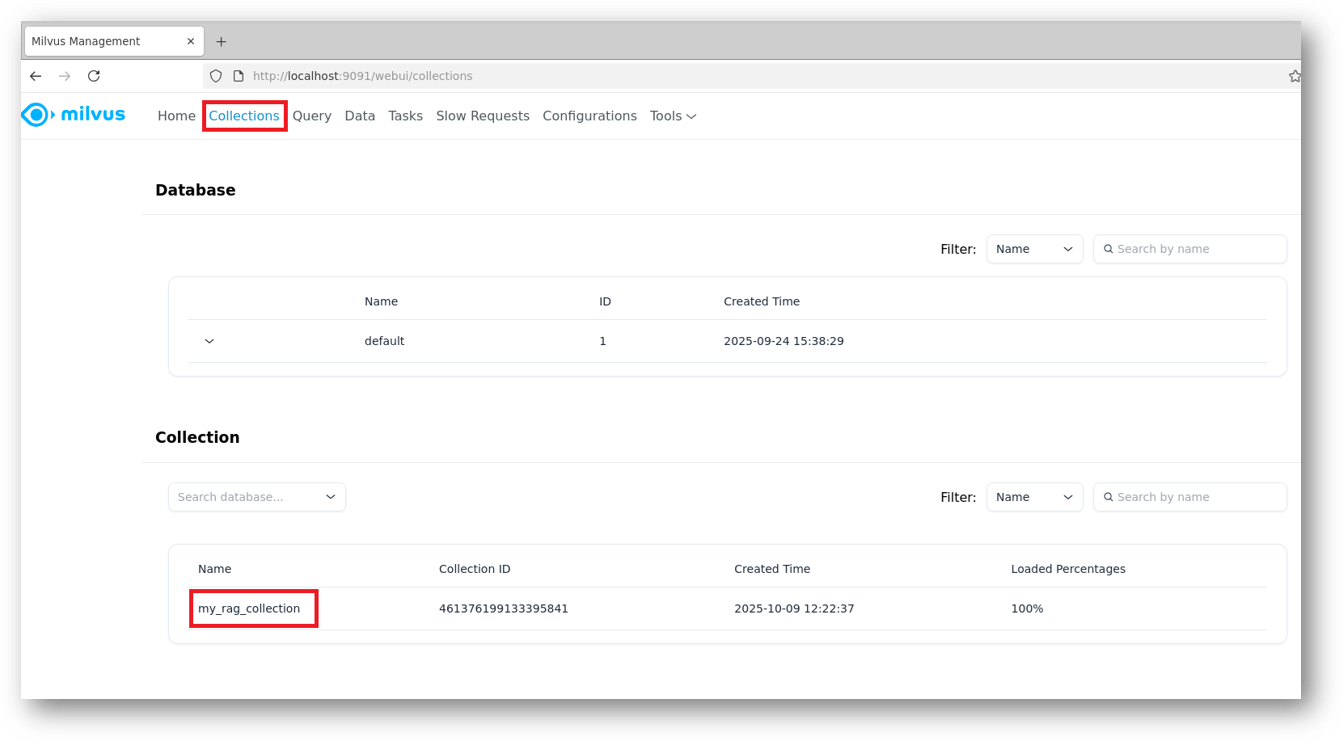
- You can access the Milvus WebUI via RDP session Browser as explained above or if you made it publicly available using your public IP of the VM, and can check the new values got inserted into your Milvus DB after execution of this Example demo.
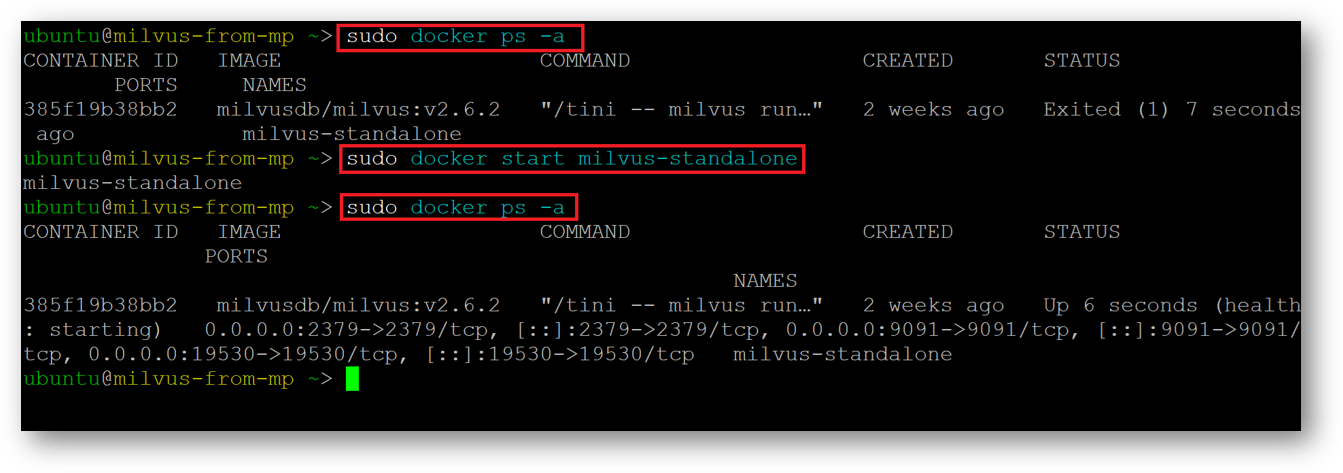
- If suppose at any point of running this example you get a connection error, or if any cell is not working then please check the running status of milvus Docker container. For that connect via SSH terminal of this VM and run below command.
If it shows container in exited state, then restart it using:
sudo docker start milvus-standalone
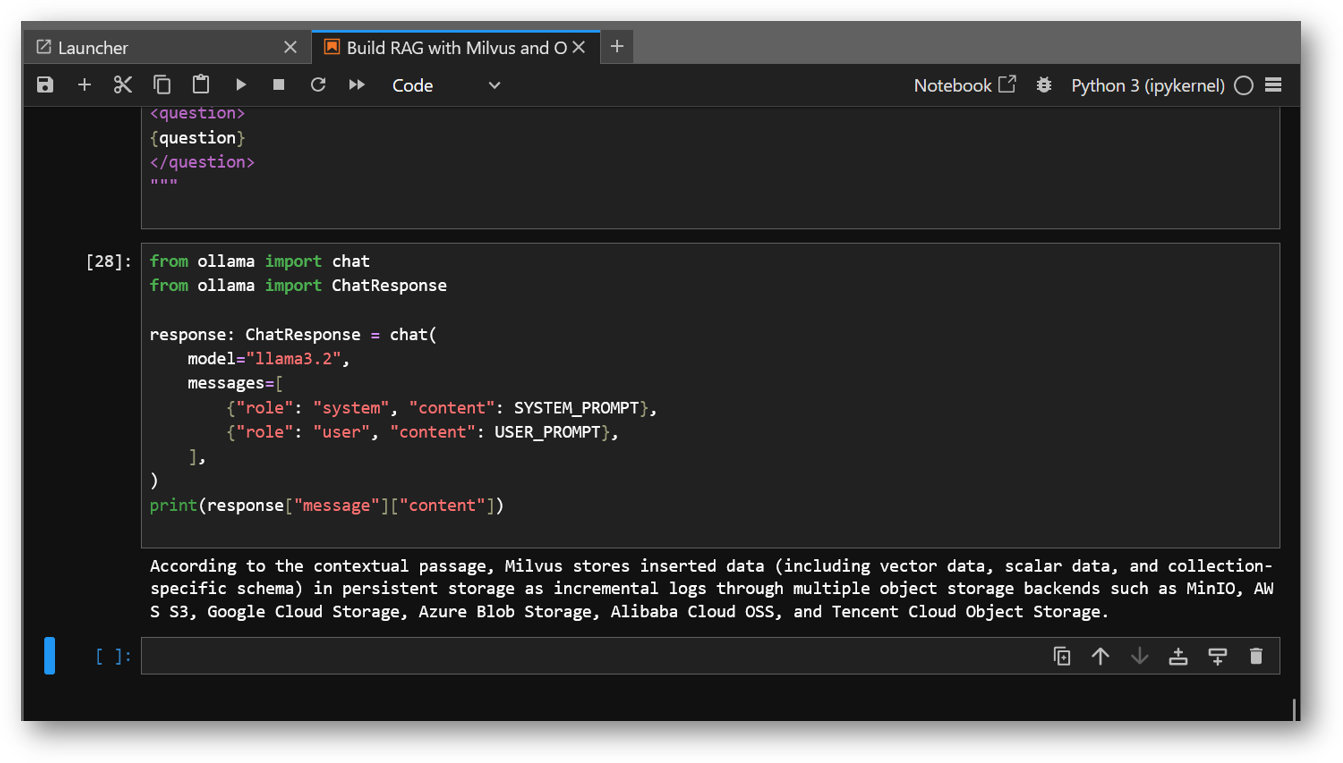
- In this Example demo we used milvus documentation and asked a specific query for “How is data stored in milvus?”, However you can play around by updating this example with other values and see how it works in real time.
For more details, please visit Official Documentation page



































