This section describes how to provision and connect to ‘Effortless Deployments on Kubernetes with Argo-CD’ VM solution on GCP.
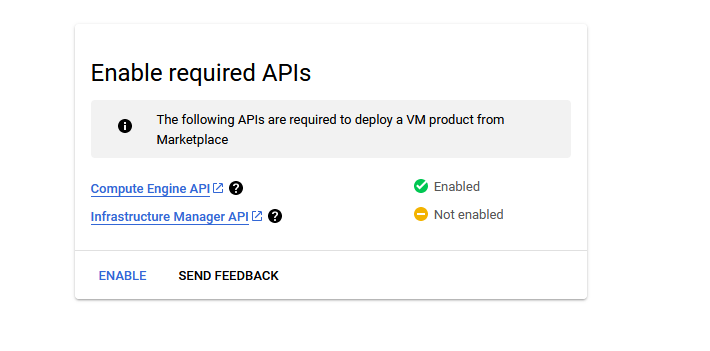
It will ask you to enable the API’s if they are not enabled already for your account. Please click on enable as shown in the screenshot.
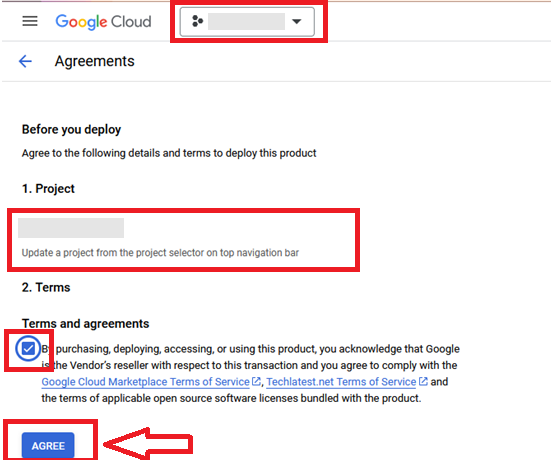
It will take you to the agreement page. On this page, you can change the project from the project selector on top navigator bar as shown in the below screenshot.
Accept the Terms and agreements by ticking the checkbox and clicking on the AGREE button.
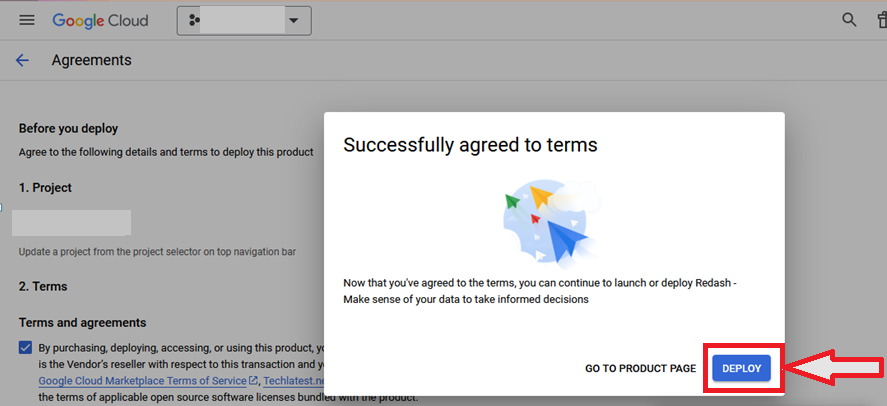
It will show you the successfully agreed popup page. Click on Deploy.
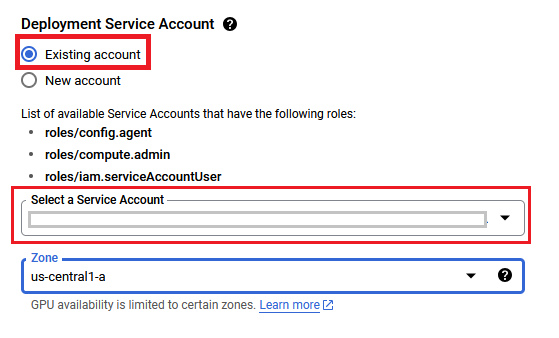
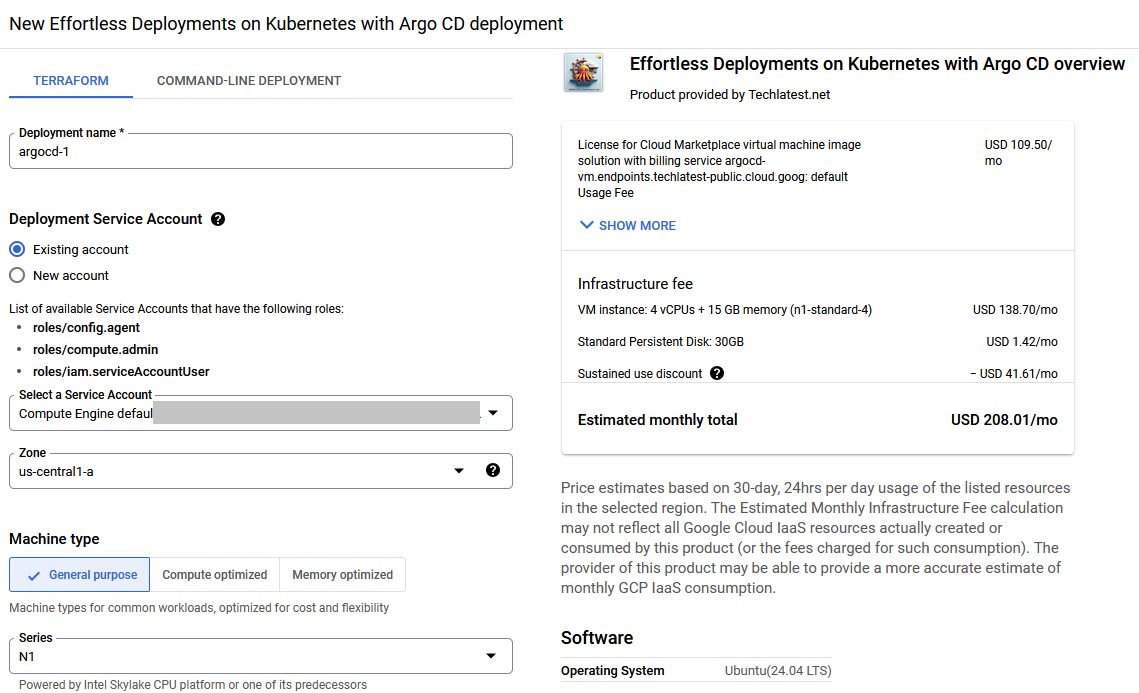
On deployment page, give a name to your deployment.
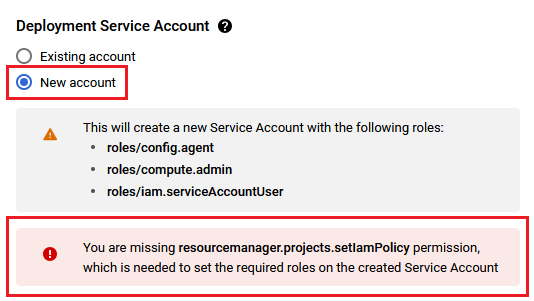
You are missing resourcemanager.projects.setIamPolicy permission, which is needed to set the required roles on the created Service Account
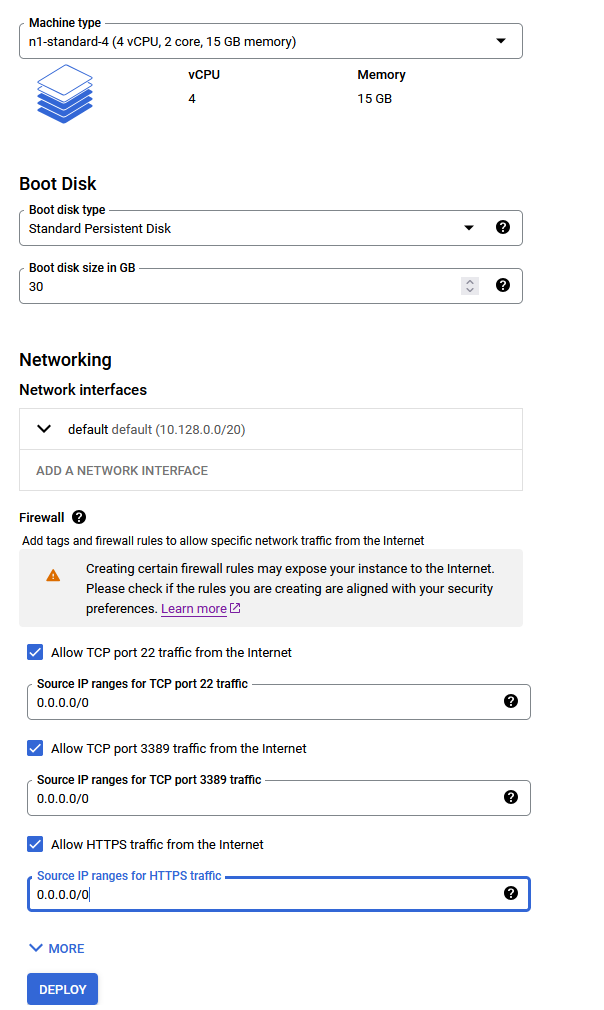
Select a zone where you want to launch the VM(such as us-east1-a)
Optionally change the number of cores and amount of memory. ( This defaults to 4 vCPUs and 15 GB RAM)
Optionally change the boot disk type and size. (This defaults to ‘Standard Persistent Disk’ and 30 GB respectively)
Optionally change the network name and subnetwork names. Be sure that whichever network you specify has ports 22 (for ssh), 3389 (for RDP) and 443 (for HTTPS) exposed.
Click Deploy when you are done.
Effortless Deployments on Kubernetes with Argo CD will begin deploying.
A summary page displays when the compute engine is successfully deployed. Click on the Instance link to go to the instance page .
On the instance page, click on the “SSH” button, select “Open in browser window”.
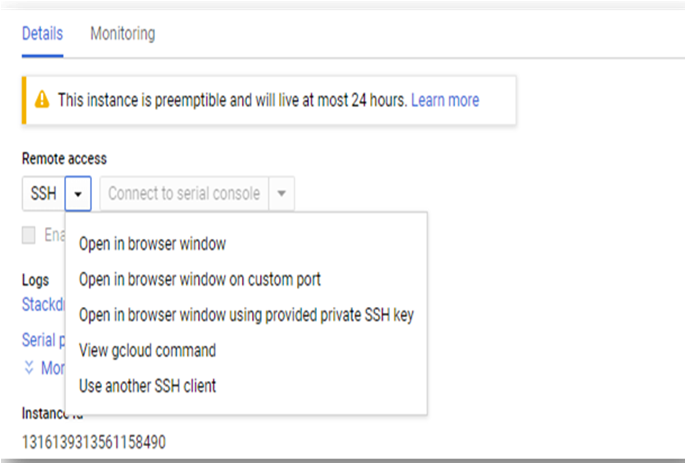
sudo passwd ubuntu
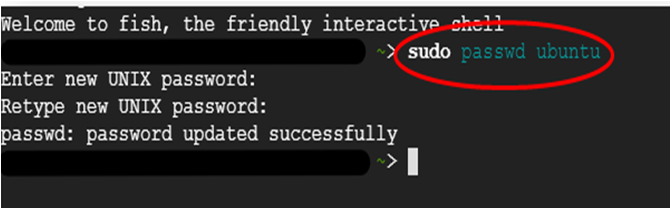
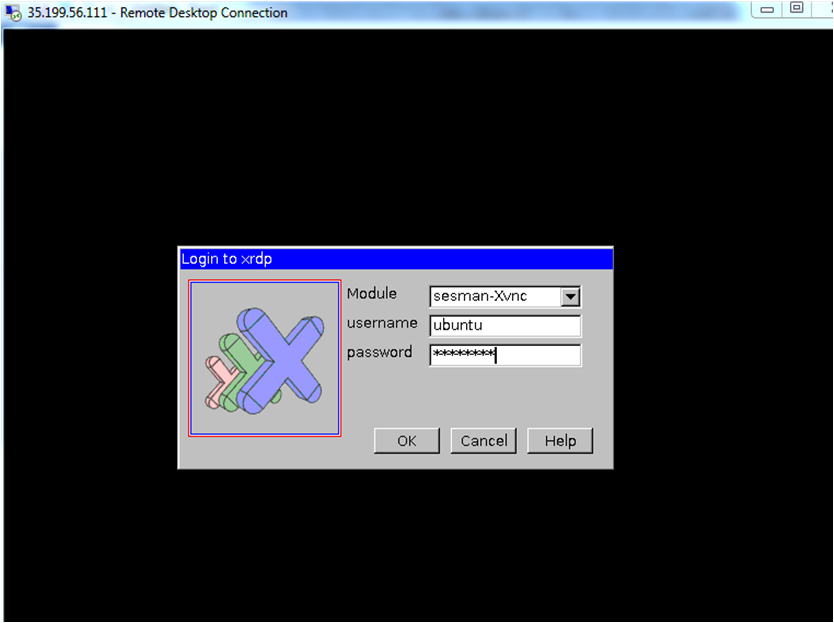
Now the password for ubuntu user is set, you can connect to the VM’s desktop environment from any local windows machine using RDP or linux machine using Remmina.
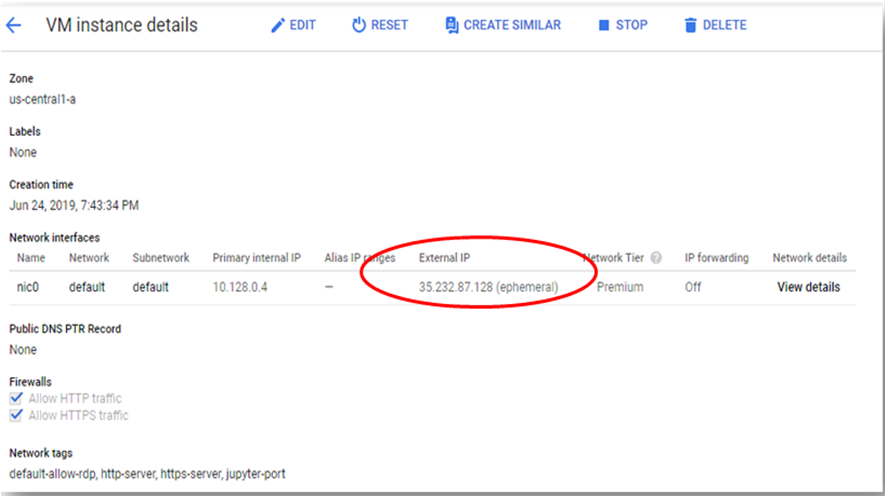
To connect using RDP via Windows machine, first note the external IP of the VM from VM details page as highlighted below
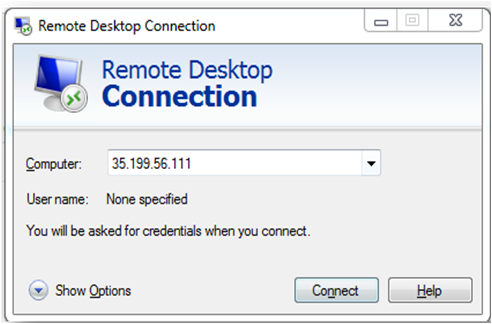
Then From your local windows machine, goto “start” menu, in the search box type and select “Remote desktop connection”
In the “Remote Desktop connection” wizard, paste the external ip and click connect

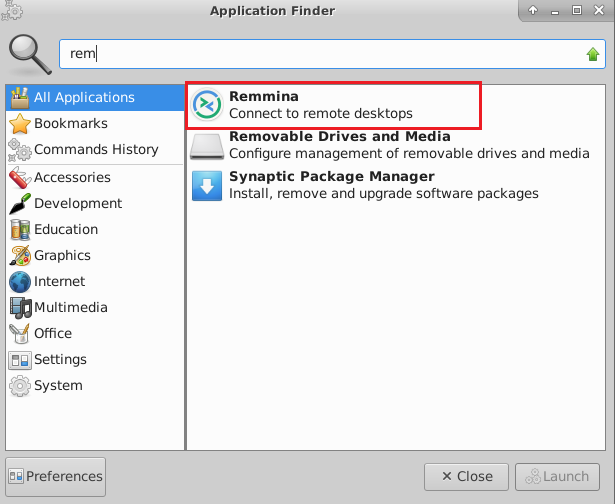
To connect using RDP via Linux machine, first note the external IP of the VM from VM details page,then from your local Linux machine, goto menu, in the search box type and select “Remmina”.
Note: If you don’t have Remmina installed on your Linux machine, first Install Remmina as per your linux distribution.
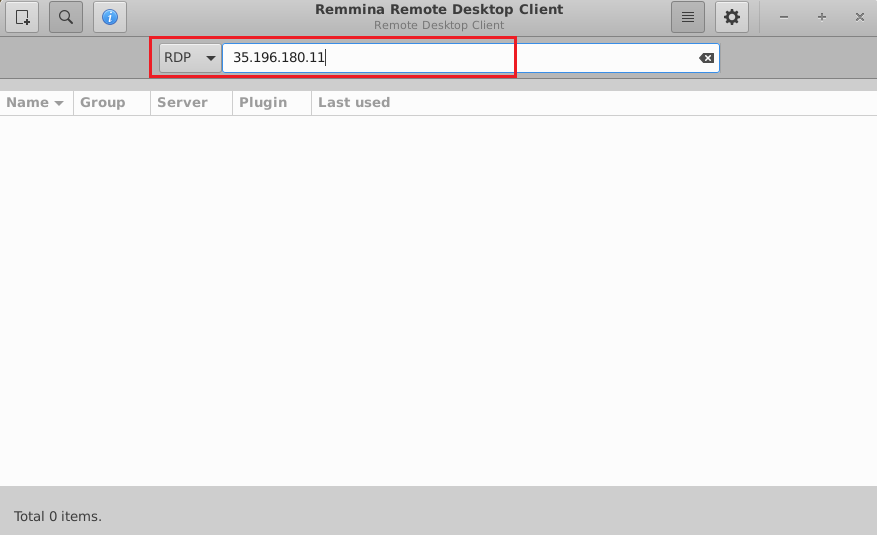
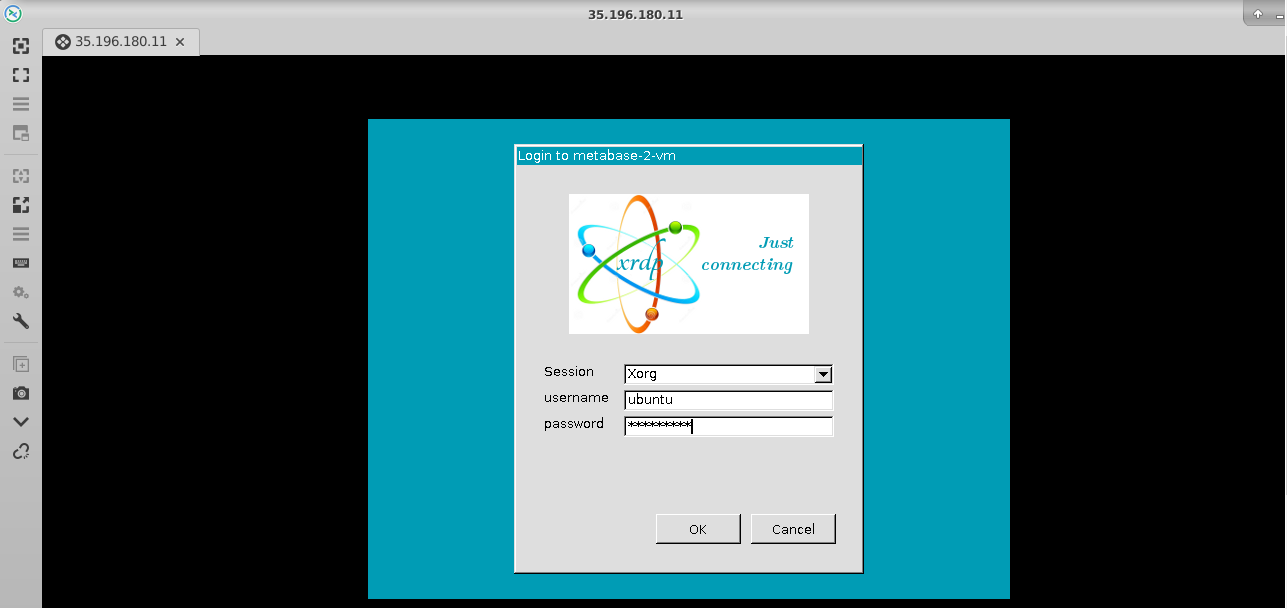

NOTE: If you are getting time out error or UI is not coming then please wait 5-10 minutes and try again.
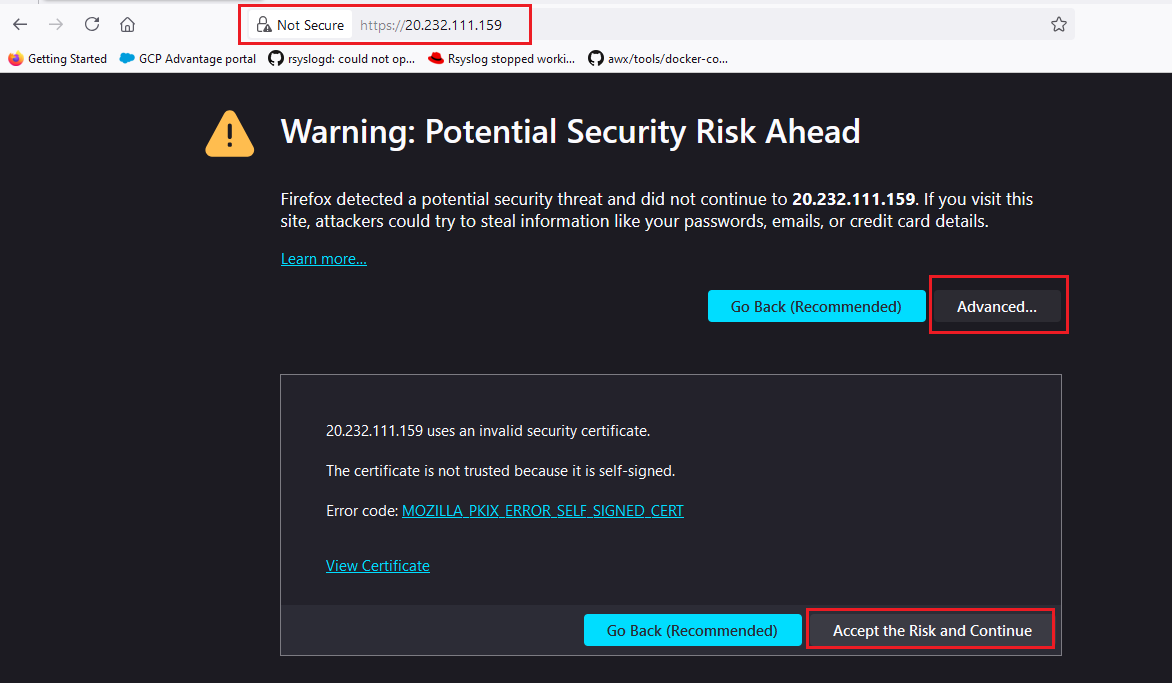
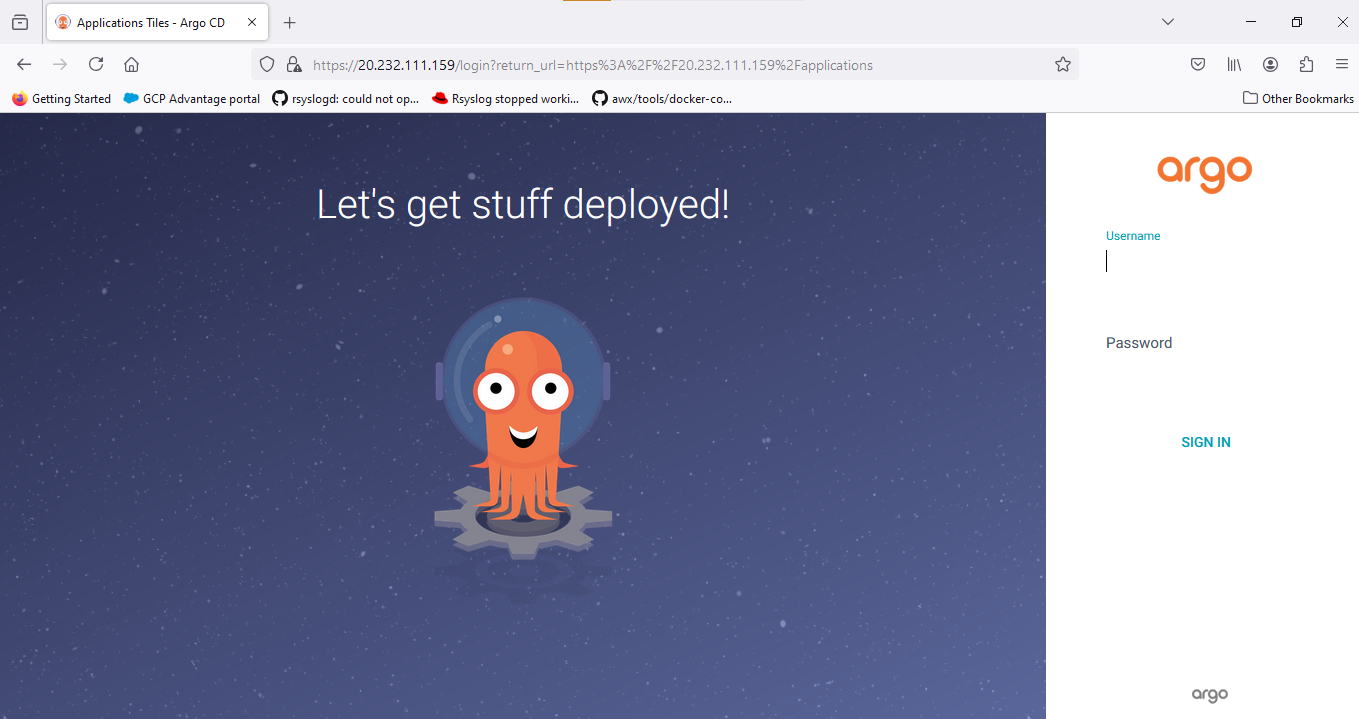
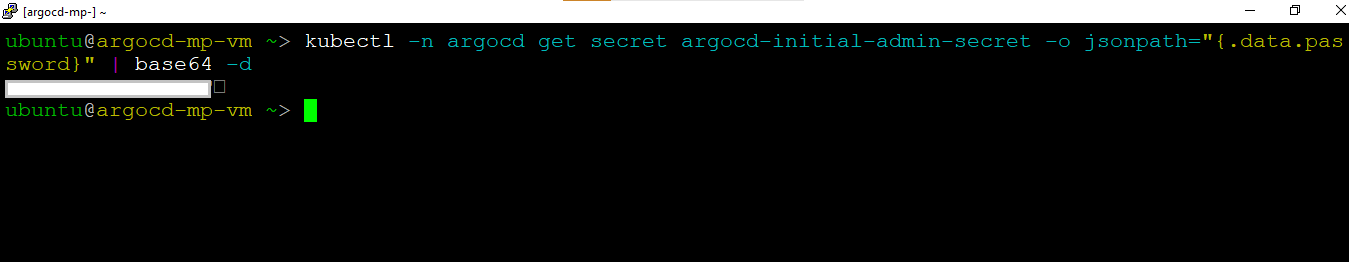
kubectl -n argocd get secret argocd-initial-admin-secret -o jsonpath="{.data.password}" | base64 -d
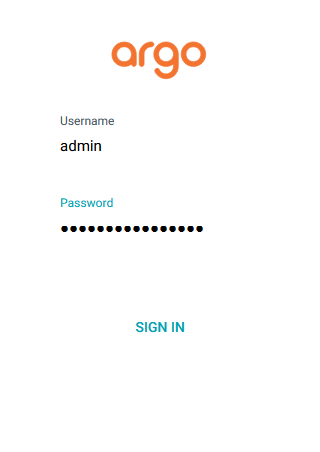
For more details please refer to ARGO-CD Official documentation