Setup and installation of 'DevOps Automation Powered by License Free Ansible & Semaphore web UI' on Azure
This section describes how to launch and connect to ‘DevOps Automation Powered by License Free Ansible & Semaphore web UI’ VM solution on Azure.
- Open DevOps Automation Powered by License Free Ansible & Semaphore web UI VM listing on Azure Marketplace.
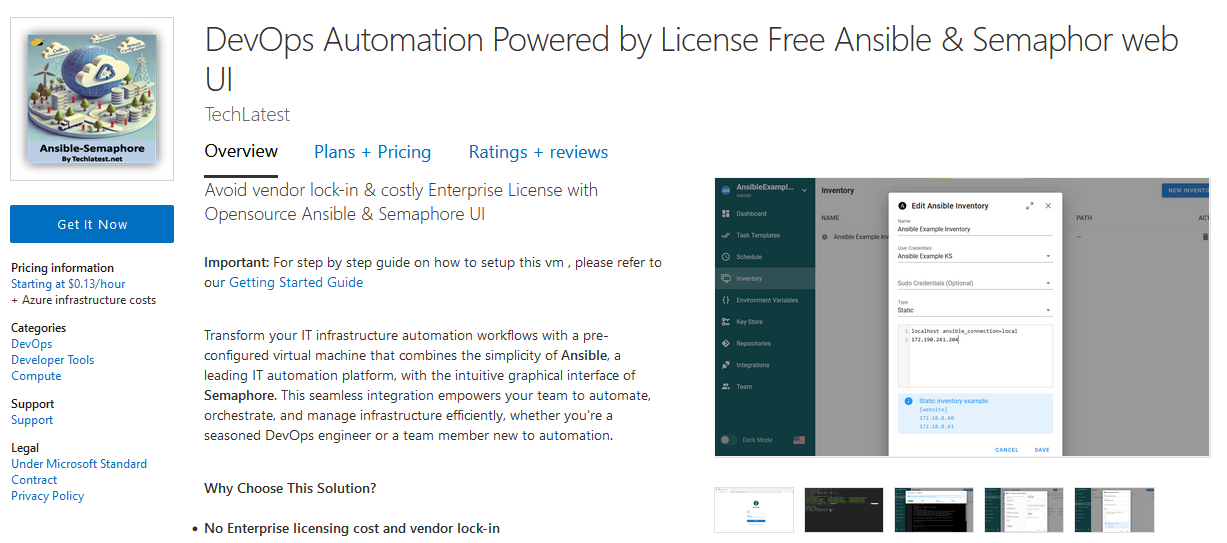
- Click on Get It Now
-
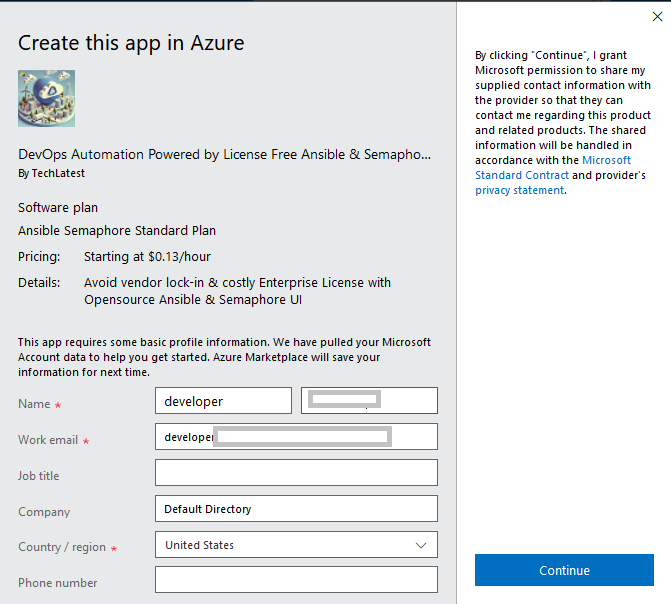
Login with your credentials, provide the details here. Once done click on Continue.
-
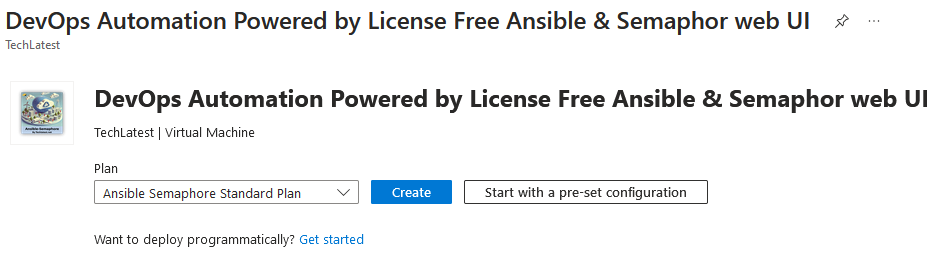
It will take you to the Product details page. Click on Create.
-
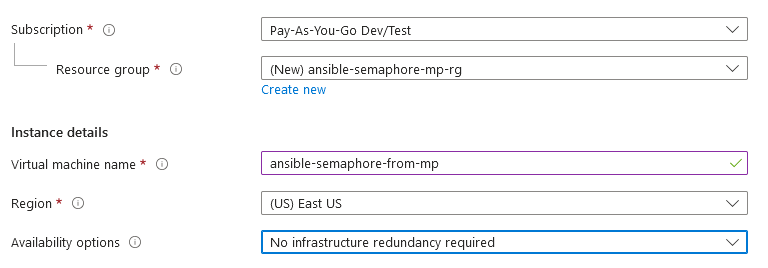
Select a Resource group for your virtual machine
-
Select a Region where you want to launch the VM(such as East US)
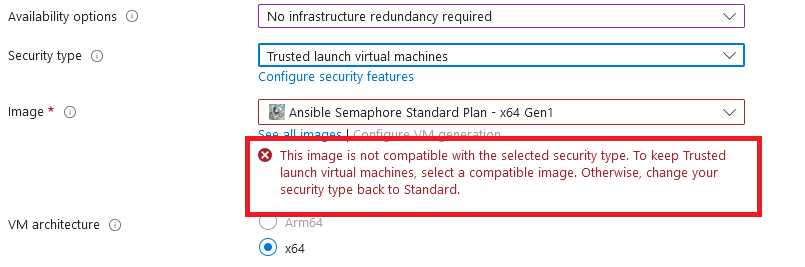
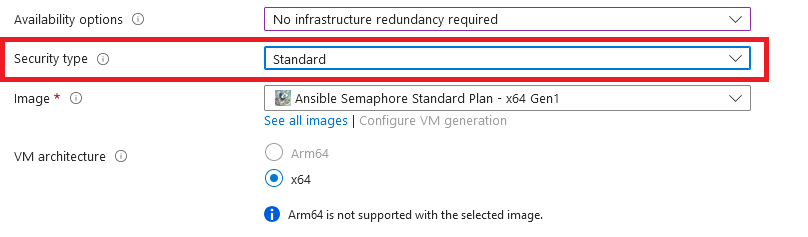
- Note: If you see “This image is not compatible with selected security type. To keep trusted launch virtual machines, select a compatible image. Otherwise change your security type back to Standard” error message below the Image name as shown in the screenshot below then please change the Security type to Standard.
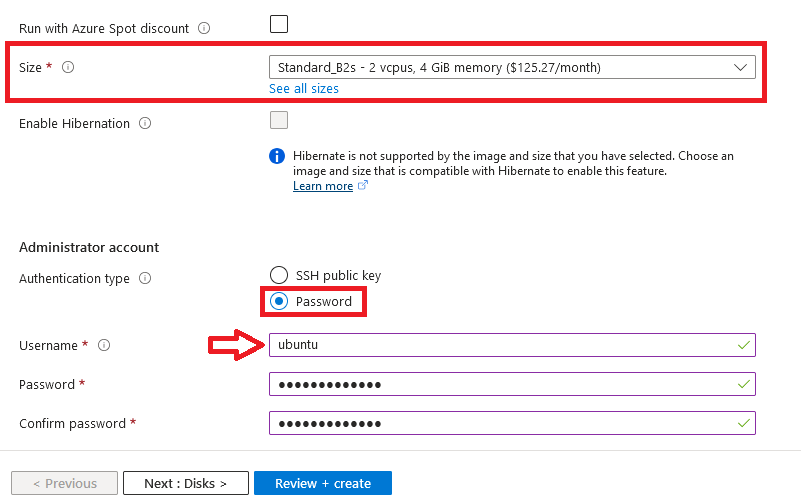
- Optionally change the number of cores and amount of memory.
Select the Authentication type as Password and enter Username as ubuntu and Password of your choice.
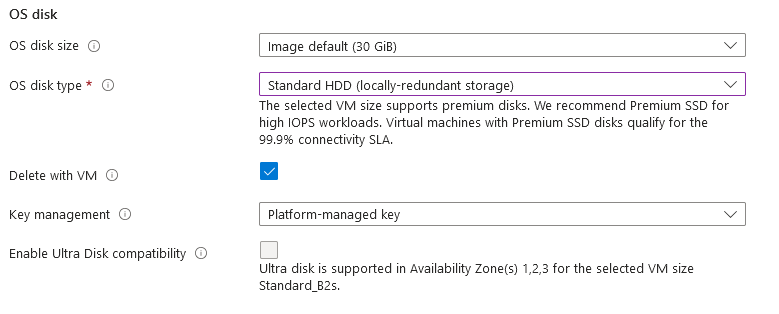
- Optionally change the OS disk size and its type.
- Optionally change the network and subnetwork names. Be sure that whichever network you specify has ports 22 (for ssh), 3389 (for RDP) and 443 (for HTTPS) exposed.
The VM comes with the preconfigured NSG rules. You can check them by clicking on Create New option available under the security group option.
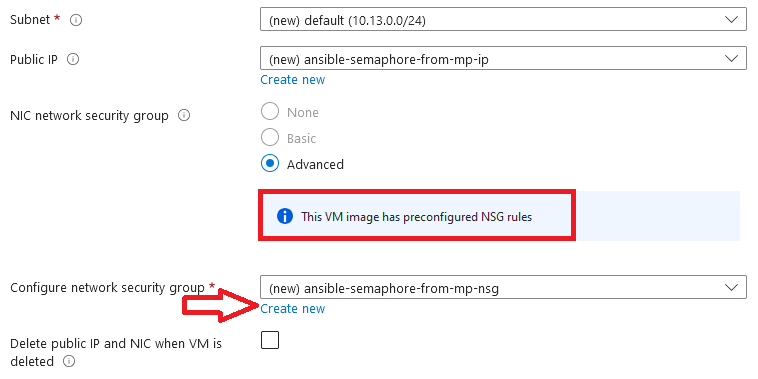
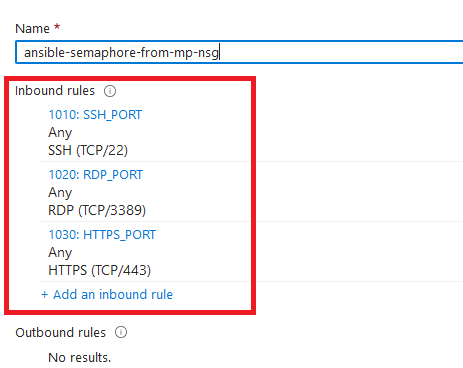
- Optionally go to the Management, Advanced and Tags tabs for any advance settings you want for the VM.
- Click on Review + create and then click on Create when you are done.
Virtual Machine will begin deploying.
- A summary page displays when the virtual machine is successfully created. Click on Go to resource link to go to the resource page. It will open an overview page of virtual machine.
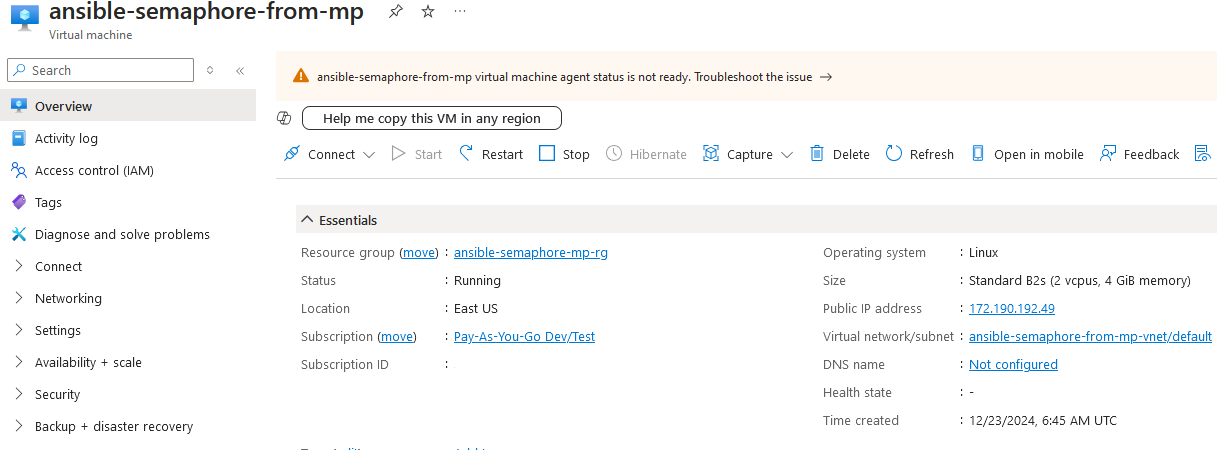
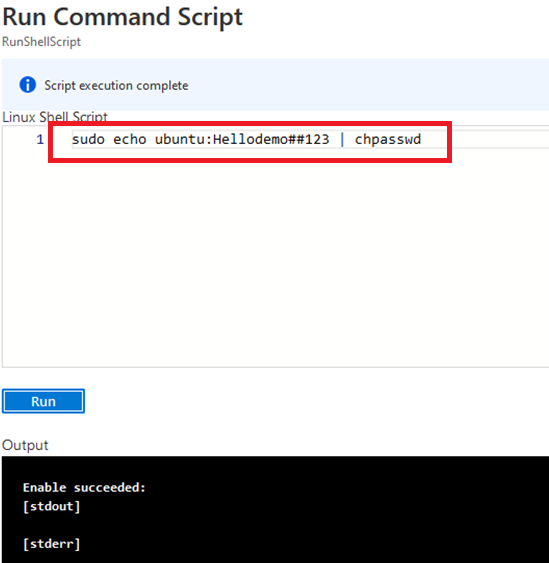
- If you want to update your password then open up the left navigation pane, select Run command, select RunShellScript and enter following command to change the password of the vm .
sudo echo ubuntu:yourpassword | chpasswd
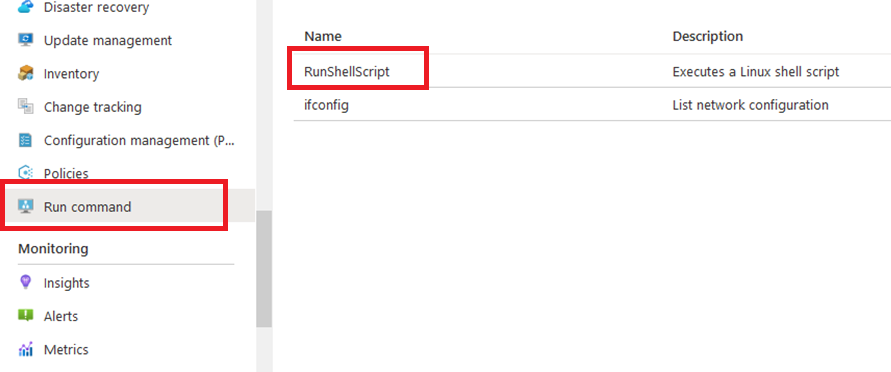
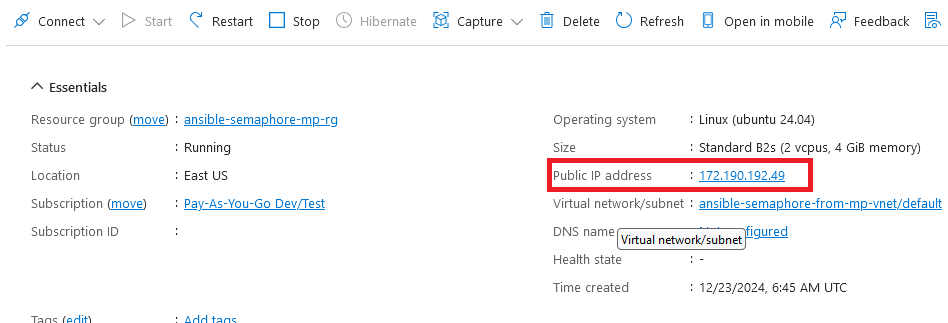
Now the password for ubuntu user is set, you can SSH to the VM. To do so, first note the public IP address of the VM from VM details page as highlighted below
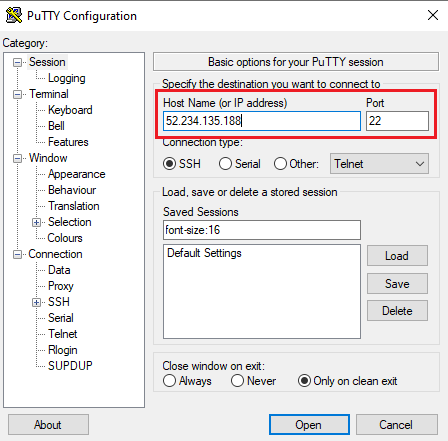
Open putty, paste the IP address and click on Open.
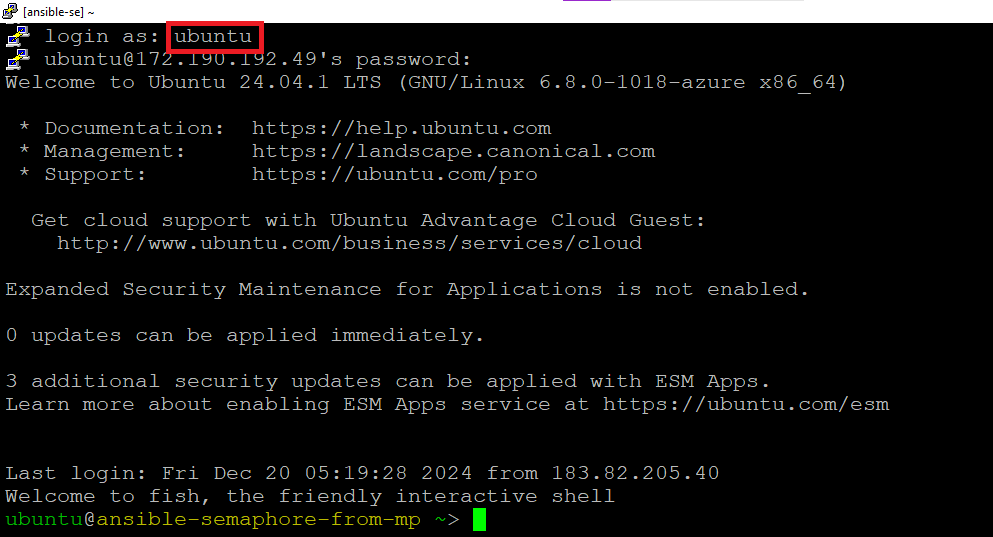
login as ubuntu and provide the password for ‘ubuntu’ user.
-
You can also connect to the VM’s desktop environment from any local windows machine using RDP protocol or local linux machine using Remmina.
-
To connect using RDP via Windows Machine, first note the public IP address of the VM from VM details page as highlighted below

- Then From your local windows machine, goto “start” menu, in the search box type and select “Remote desktop connection”.
In the “Remote Desktop connection” wizard, copy the public IP address and click connect
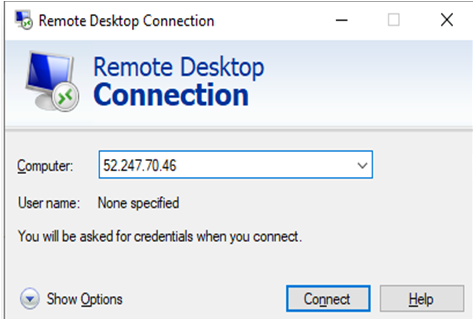
- This will connect you to the VM’s desktop environment. Provide the username (e.g “ubuntu”) and the password set in the step4 to authenticate. Click OK
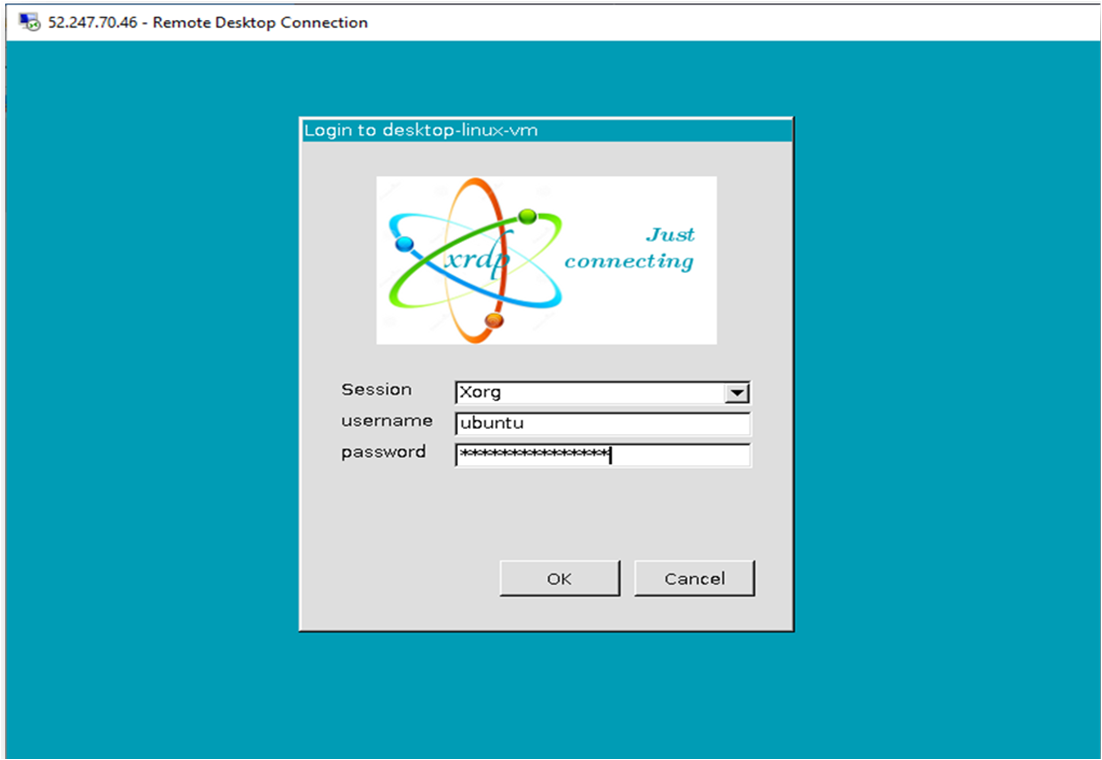
- Now you are connected to the out of box DevOps Automation Powered by License Free Ansible & Semaphore web UI VM’s desktop environment via Windows Machine.

- To connect using RDP via Linux machine, first note the external IP of the VM from VM details page, then from your local Linux machine, goto menu, in the search box type and select “Remmina”.
Note: If you don’t have Remmina installed on your Linux machine, firstInstall Remmina as per your linux distribution.
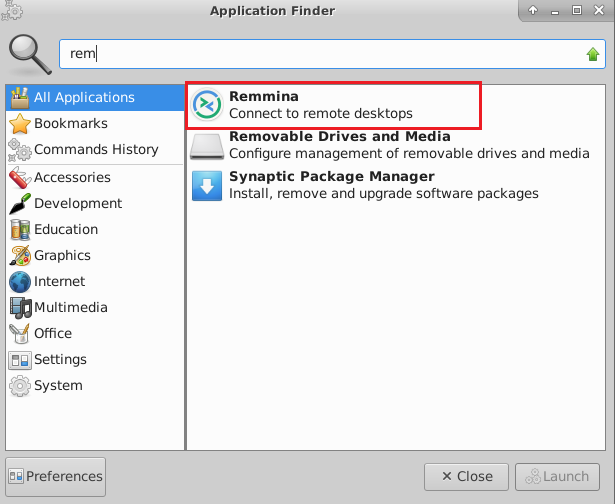
- In the “Remmina Remote Desktop Client” wizard, select the RDP option from dropdown and paste the external ip and click enter.
- This will connect you to the VM’s desktop environment. Provide “ubuntu” as the userid and the password set in above reset password step to authenticate. Click OK
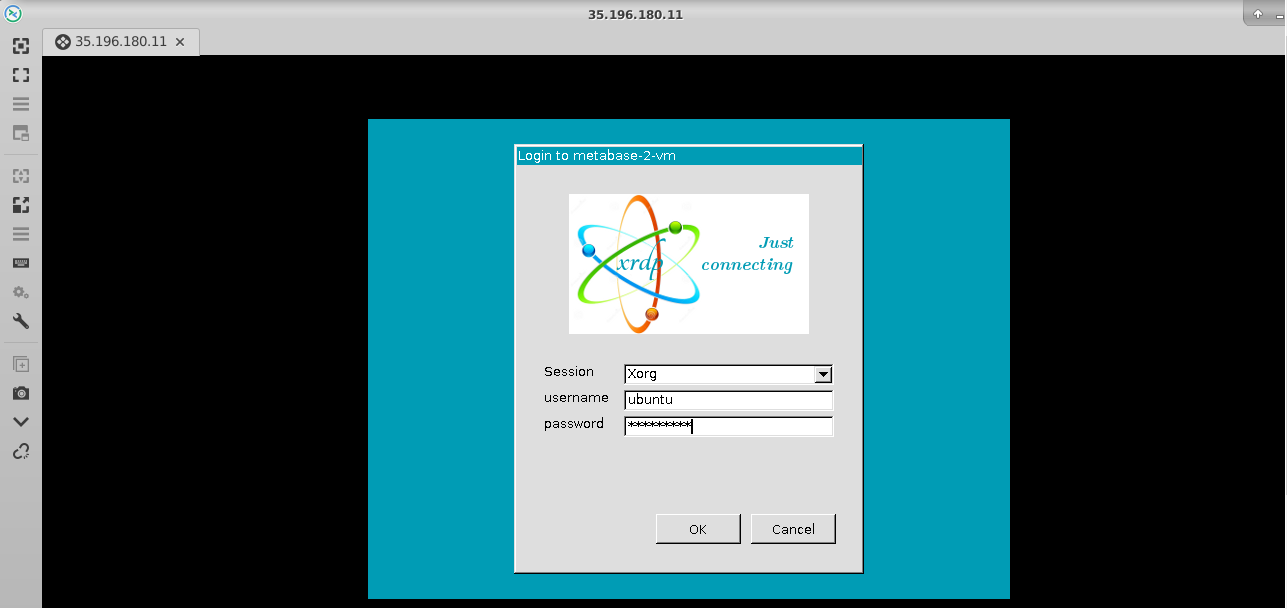
- Now you are connected to out of box DevOps Automation Powered by License Free Ansible & Semaphore web UI VM’s desktop environment via Linux machine.

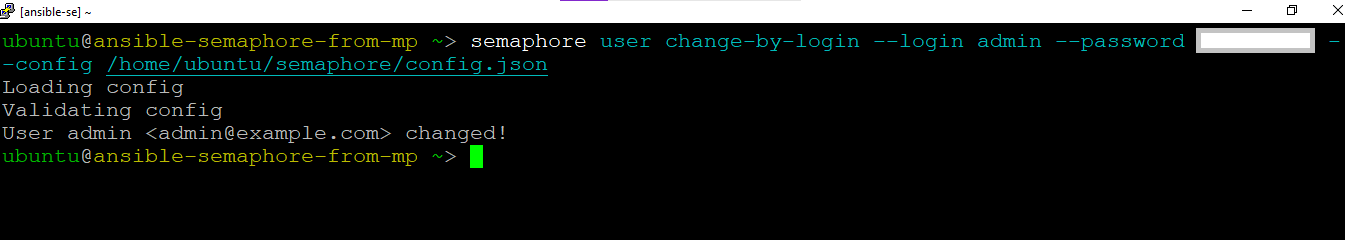
- To access the Semaphore Web Interface, first reset semaphore admin password by running below command in the SSH terminal -
Replace NEWPASSWORD with your desired password here.
semaphore user change-by-login --login admin --password NEWPASSWORD --config /home/ubuntu/semaphore/config.json
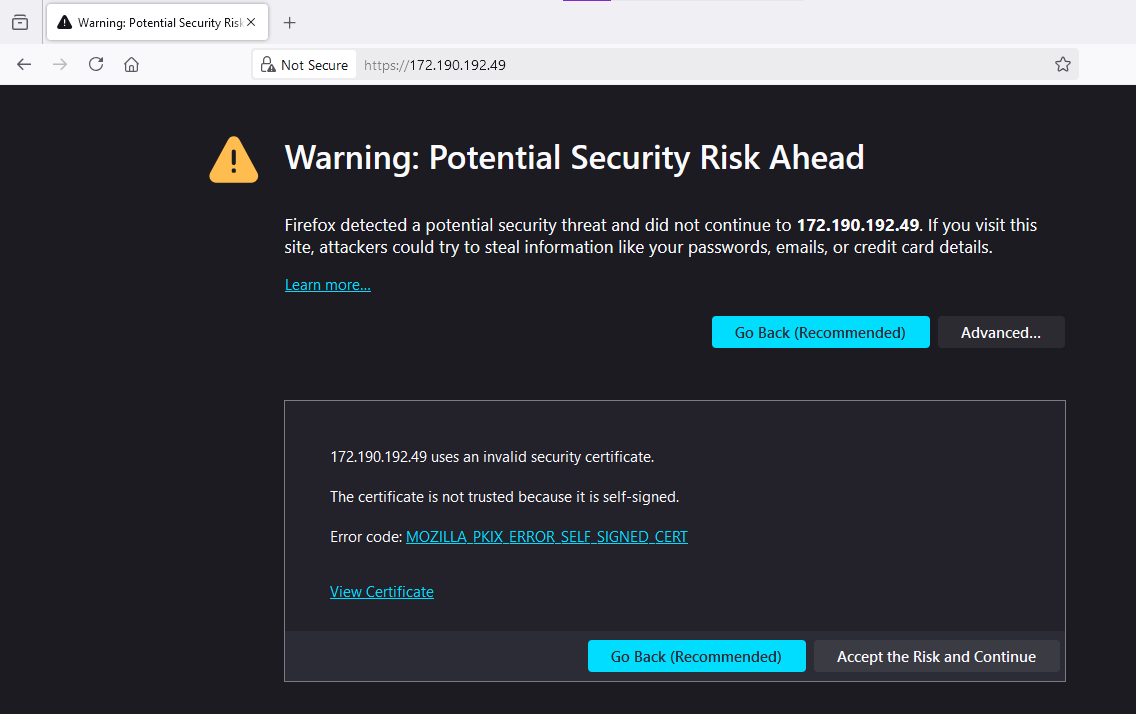
- Once Semaphore password is ready, copy the public ip of the vm from VM’s details page and paste it in the browser using https://VM_Public_IP. Make sure to use https and not http.

Browser will display a SSL certificate warning message. Accept the certificate warning and Continue.
- Login with admin user and provide the password set in above step.
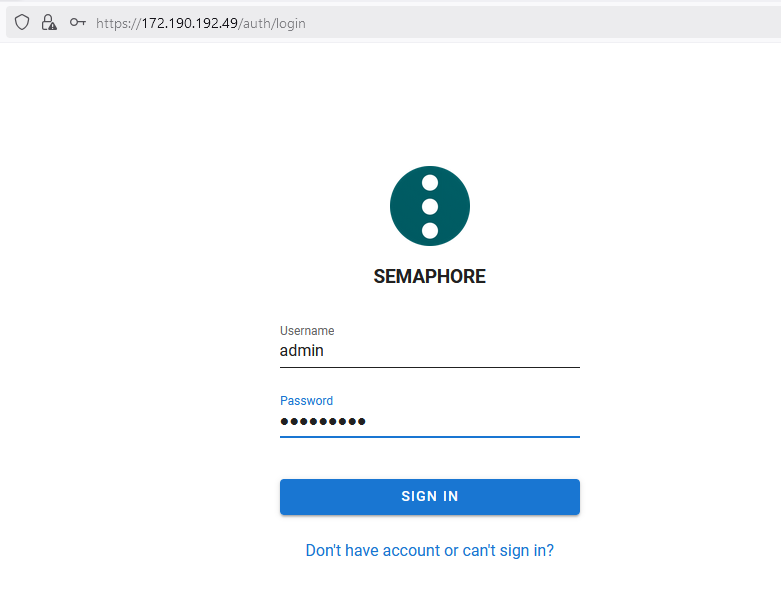
- Now you are logged in to Semaphore Web Interface where you can manage Ansible automation task.
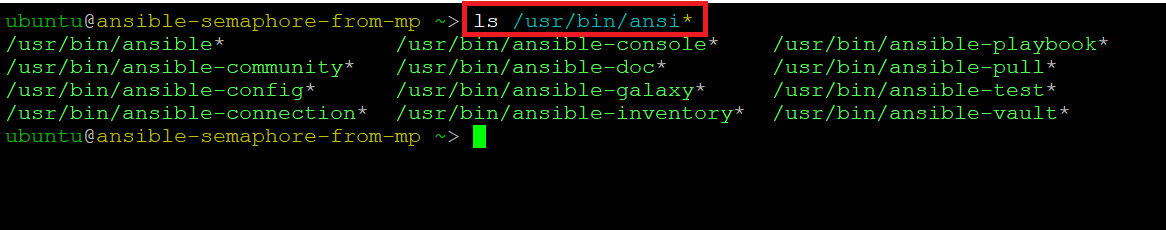
- The VM comes with various Ansible modules preconfigured out of the box for you. The Ansible executable are located at /usr/bin/ directory. You can access these files and folders from SSH or RDP sessions.
ansible-community
- ansible-community allows users to manage, install, and use Ansible collections created and shared by the community, typically available through Ansible Galaxy.
ansible-config
- The ansible-config executable is a command-line tool in Ansible that helps manage configuration settings. It allows users to view, validate, and edit Ansible’s configuration files (ansible.cfg).
ansible-connection
- The ansible-connection is used to manage and handle connections between Ansible and remote systems. It helps configure the connection type (like SSH, local, or others) and allows troubleshooting or testing of connection-related issues during automation tasks.
ansible-console
- The ansible-console provides an interactive command-line interface (CLI) for running Ansible commands and playbooks. It allows users to interactively execute Ansible tasks, explore modules, and test playbooks in a live environment.
ansible-doc
- The ansible-doc is a command-line tool used to view documentation for Ansible modules, plugins, and other components. It allows users to quickly access detailed information about a module’s usage, options, and examples directly from the terminal.
ansible-galaxy
- The ansible-galaxy is a command-line tool used to interact with Ansible Galaxy, a hub for sharing and discovering Ansible roles, collections, and content. With this tool, users can search for, install, create, and manage roles and collections that can be used in Ansible playbooks to automate tasks across different systems.
ansible-inventory
- The ansible-inventory is a command-line tool used to manage and view Ansible inventories. It allows users to display, generate, and validate the inventory of managed hosts (either from static files or dynamic sources).
ansible-playbook
- The ansible-playbook is used to run Ansible playbooks, which are YAML files that define a series of automation tasks. This tool allows users to execute configurations, deployments, and orchestrations across multiple systems by reading the playbook and applying the defined tasks to the target hosts.
ansible-pull
- The ansible-pull is used to pull Ansible playbooks from a remote repository (like Git) and apply them to the local machine. It runs the playbooks in reverse from the typical Ansible model: instead of Ansible pushing configurations to remote machines.
ansible-vault
- The ansible-vault is used to encrypt and decrypt sensitive data in Ansible. It allows users to securely store secrets, such as passwords or API keys, within Ansible playbooks and variables.
ansible-test
- The ansible-test is used for testing and validating Ansible code, such as modules, plugins, and collections. It helps developers run unit tests, integration tests, and linting checks to ensure the quality and correctness of their Ansible code.
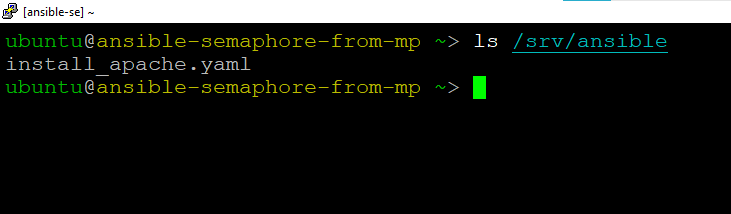
- Ansible base repository for ansible example playbook is localted at /srv/ansible.
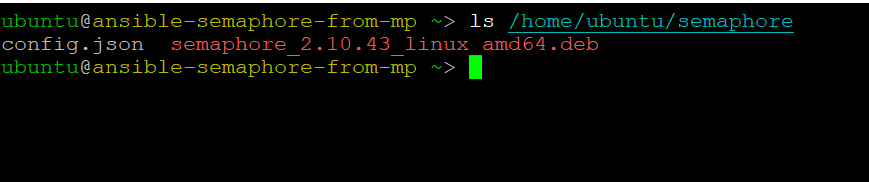
- Semaphore config directory is /home/ubuntu/semaphore.
If you want to further configure Ansible then please visit How to run Ansible Playbooks from Semaphore UI page.
For more details on Ansible or Semaphore please refer to Official Documentation Page































